advertisement
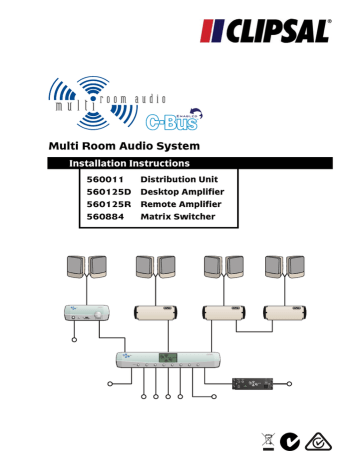
Multi Room Audio System
Installation Instructions
POWER
MUTE
ZONES
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
AUDIO R AUDIO L
DC 24V
INPUT
POWER
IR
DIGITAL
AUDIO
OUTPUT
© Copyright Clipsal Integrated Systems Pty Ltd 2005. All rights reserved. This material is copyright under Australian and international laws. Except as permitted under the relevant law, no part of this work may be reproduced by any process without prior written permission of and acknowledgement to Clipsal Integrated
Systems Pty Ltd.
Clipsal is a registered trademark of Clipsal Australia Pty Ltd.
The information in this manual is provided in good faith. Whilst Clipsal Integrated
Systems (CIS) has endeavoured to ensure the relevance and accuracy of the information, it assumes no responsibility for any loss incurred as a result of its use.
CIS does not warrant that the information is fit for any particular purpose, nor does it endorse its use in applications which are critical to the health or life of any human being. CIS reserves the right to update the information at any time without notice.
V1.0 Dec 2005
Contents
5.0 Installation and Connection
5.2
5.6
5.7 Shielded Audio Cabling
6.0 C-Bus System Clock
7.0 C-Bus Network Burden
10.0 Programming and Setup
Multi Room Audio System
13.4 System Audio Performance
4
Installation Instructions
Catalogue Number
560011
560125D
560125R
560884
5600P24/500AU
5600P24/3750AU
Description
Multi Room Audio Distribution Unit
Multi Room Audio Desktop Amplifier
Multi Room Audio Remote Amplifier
Multi Room Audio Matrix Switcher
MRA Distribution Unit Power Supply
MRA Amplifier Power Supply Unit
AUDIO R AUDIO L
DC 24V
INPUT
POWER
Distribution Unit (DU)
IR
DIGITAL
AUDIO
OUTPUT
Power Supply
(PS) for DU
Switch Mode Power Supply
Unit (PSU) for Amplifiers
POWER
MUTE
Desktop Amplifer Remote Amplifier
ZONES
1 2 3 4 5
Matrix Switcher
6
Figure 1 – Multi Room Audio product identification
7 8
5
Multi Room Audio System
• The Matrix Switcher has a built-in C-Bus power supply. Take this into account when determining the power supply requirement of the
C-Bus network.
• Avoid laying analogue or digital audio cable alongside mains cable, to minimise EMI interference and signal disruption.
• Do not cover or block the vents on the Matrix Switcher enclosure.
• The Matrix Switcher and Amplifiers of a particular Multi Room Audio
(MRA) system must be connected to the same C-Bus network.
Multiple MRA systems may reside on separate C-Bus networks.
• Only use a Clipsal approved power supply to power an MRA Amplifier or Distribution Unit. Failure to do so may damage the unit, and void the warranty.
• Units must be installed in accordance with local authority guidelines.
• The digital audio outputs must only be used with MRA Amplifiers.
The Multi Room Audio Matrix Switcher and Amplifiers provide a C-Bus enabled audio distribution system.
The Matrix Switcher is installed in a room together with audio sources such as a radio tuner, CD player and digital TV set top box. Connections are made to the Amplifiers and to C-Bus.
Amplifiers are installed in each room where audio is to be distributed.
They are connected to speakers and the C-Bus network. Using C-Bus switches (or the controls on a Desktop Amplifier), each Amplifier can select different audio sources and adjust the volume, bass and treble.
The Distribution Unit allows a single stereo audio input to be added to the digital input of the Matrix Switcher. It also allows one distributable stereo audio input to be plugged into the Amplifiers when no Matrix Switcher is used (when Amplifiers are used in stand-alone mode).
A typical Multi Room Audio system distributes up to four stereo analogue audio inputs (five if a Distribution Unit is used), and one stereo optical digital audio input. These inputs are distributed to up to 8 zones (each consisting of one or more Amplifiers). A special mono audio input can be
6
Installation Instructions used to broadcast a message to all zones. Additionally each Amplifier is capable of accepting a local stereo audio input, providing up to seven stereo audio channels for each Amplifier.
By adding infrared (IR) targets and emitters to the system, Amplifiers can distribute infrared remote control signals to audio source equipment via the Matrix Switcher. Additionally two buttons on a C-Bus wall switch can be configured to send infrared commands to the audio source equipment; commands which adapt according to which source is selected.
A Multi Room Audio system can be installed in either a matrix or standalone configuration.
4.1 Matrix
A matrix configuration (Figure 2) consists of a Matrix Switcher which is
connected to one or more Multi Room Audio Amplifiers. An Amplifier connected to each zone can select from up to six stereo audio sources plus its local stereo audio input. The audio broadcast and annunciation features of the Matrix Switcher can be utilised in this configuration.
Multi Room Audio Amplifiers
POWER MUTE
DIn
Local audio input
DOut
Broadcast audio input
DIn DIn
DOut
Matrix Switcher DOut
DOut
ZONES
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
DIn Distr’n Unit
AUDIO R AUDIO L IR
DIGITAL
AUDIO
OUTPUT
POWER
DC 24V
INPUT
DIn
PSU
Analogue audio input
PS
Analogue audio inputs
Optical digital audio input
Notes:
Audio inputs are stereo with the exception of Broadcast.
Using a Distribution Unit with the Matrix Switcher provides an additional stereo analogue audio input.
DIn – Digital Audio In
DOut – Digital Audio Out
Figure 2 – The matrix confguration
7
Multi Room Audio System
4.2 Standalone
In a standalone configuration a stereo audio source is connected to the input of a Distribution Unit. The output of the Distribution Unit is connected to the digital input of each Amplifier. RJ45 splitters are used to connect all digital inputs to a common Cat-5 cable run. A Matrix Switcher is not used. Up to eight Amplifiers can be connected in this mode using a
total cable length of up to 45 m. This is illustrated in Figure 3. Each
Amplifier can select between the single distributed stereo audio source and its local stereo audio input.
Multi Room Audio Amplifiers
Analogue audio input
Distr’n Unit
AUDIO R AUDIO L IR
DIGITAL
AUDIO
OUTPUT
DC 24V
INPUT
POWER
PSU
POWER
MUTE
DIn P
PSU
DIn P
PSU
DIn P LIn
Local audio input
Notes:
Audio inputs are stereo.
Do not connect a Power Supply to the Distribution Unit when it is connected to an Amplifier’s Digital Input. In this configuration, the Distribution Unit receives its power from the Amplifier.
DIn – Digital Audio In
LIn – Local In
P – Power input
Figure 3 – Standalone configuration
8
Installation Instructions
5.0 Installation and Connection
The most time consuming stage of installing a typical Multi Room Audio system is likely to be cabling and wiring. To ensure successful wiring and connection of a Multi Room Audio system:
• Plan – Consider the way the system will be used and create drawings to indicate where terminations will be located.
• Organise – Use wall plate terminations to connect to the Matrix
Switcher, Amplifiers and speakers, as well as any local or mono broadcast inputs or headphone outputs. Label the terminations, especially the C-Bus and digital audio sockets which are both
RJ45. Consider using colour coded sockets.
• Use appropriate cable.
5.1 Location and Mounting
The Multi Room Audio Matrix Switcher, Distribution Unit, Amplifiers and their associated Power Supplies are suitable for indoor use in moderate to tropical climates. All units must be protected from excessive heat, dampness and liquids.
Matrix Switcher
It is recommended that the Matrix Switcher be located in a central location with the audio source equipment (such as in a cabinet in the lounge room).
Place the Matrix Switcher on a flat surface. Do not remove the feet from the base of the unit as they provide necessary air space. Air must be allowed to flow through vents on the top and base of the Matrix Switcher
(by natural convection). Ensure that at least 15 mm of free space is left above the unit, as well as 50 mm at the front of the unit and 75 mm at the
rear. This is illustrated in Figure 4.
Ensure that the user will have access to the mains inlet socket after the unit has been installed.
9
Multi Room Audio System
Amplifiers and Switch Mode Power Supply
Suitable locations for Amplifiers may include built-in robes, a pantry or in a ceiling space which is not subjected to high temperature. Alternatively
Amplifiers may be located centrally with the Matrix Switcher.
Air must be allowed to flow against the fins on the sides of the Amplifiers
(by natural convection). Ensure that at least 50 mm of free space is left at the rear and at each side of the Amplifiers. In addition, leave at least
10 mm of free space at the front of the Desktop Amplifier.
The Switch Mode Power Supply for the Amplifiers has a vent at one end.
Leave at least 50 mm of free space in front of this vent. Refer to Figure 5.
free space
75 mm
Matrix
Switcher free space
50 mm
15 mm
ZONES
1 2 7 8 3 4 5 free space
6
Figure 4 – Clearance must be left around the Matrix Switcher
10
8 mm
free space
Installation Instructions free space
50 mm air vent
Amplifier free space
10 mm
Switchmode
Power Supply for Amplifiers free space
POWER
MUTE
50 mm 50 mm
Figure 5 – Clearance must be left around Amplifiers and their Power Supplies
5.2 An Example System
In a Multi Room Audio (MRA) installation, you can locate an Amplifier and speakers in each room where audio is required. You would then run RJ45 cable across the building from the Matrix Switcher to each Amplifier, and run shorter lengths of cable from the Amplifiers to the speakers.
Alternatively, you can locate all Amplifiers in a central location and run the speaker cables across the building. In the example used to illustrate an
MRA system installation, a combination of these methods is used.
The example system consists of one Matrix Switcher, five Remote
Amplifiers and one Desktop Amplifier. Three of the Remote Amplifiers are collocated with the Matrix Switcher. One Remote Amplifier is located on a shelf in the Garage and another in a built-in robe (BIR). The Desktop
Amplifier is located on a desk in Bedroom 2 (BR2). Speakers are mounted on walls using appropriate brackets. Wall plates are used in the bedrooms and family room to provide local inputs. These can be used to connect to the audio output of a personal computer (PC) or portable audio player.
On the following pages, diagrams are used to illustrate the C-Bus, speaker, digital audio, IR target and shielded audio stages of the installation.
11
Multi Room Audio System
The Amplifiers and Matrix Switcher in a Multi Room Audio system must be connected to a common C-Bus network. Use Cat-5 Unshielded Twisted
Pair (UTP) C-Bus cable, and appropriately wired RJ45 plugs and wall plates.
Pinouts and cable conductor assignments are provided in Figure 6 and
Table 1. Label wall plates to differentiate between other RJ45 connection
types (such as Digital Audio and Ethernet). If colour coding, it is suggested you use pink for C-Bus, green for Digital Audio and blue for Ethernet.
Use a C-Bus wall switch (such as Ulti Saturn, Neo or Reflection) to control each zone of the Multi Room Audio system. Switches with Dynamic
Labelling Technology (DLT) can be configured to provide visual feedback of selected audio sources. Typically, an individual C-Bus wall switch is used to control both lighting and audio.
In the example installation in Figure 7, Ulti Saturn and Neo wall switches
are used in BR2 and BR3 respectively (zones 2 and 3), and DLT wall switches are used to control the remaining Multi Room Audio zones.
C-Bus Positive: blue + orange
C-Bus Negative: blue & white + orange & white
Remote OFF: brown + brown & white
Remote ON: green + green & white
Figure 6 – C-Bus cable conductor assignments
Pin
1
C-Bus Connection
Remote ON
87654321
12345678
3
4
5
6
7
C-Bus Negative (–)
C-Bus Positive (+)
C-Bus Negative (–)
C-Bus Positive (+)
Remote OFF
Colour green & white green orange & white blue blue & white orange brown & white brown
Table 1 – RJ45 sockets and C-Bus Pinouts
12
Installation Instructions
RJ45
Lounge
Family
(Zone 4)
IR
L Sw
C
Volume
DVD
Play
Skip next
M
C
Dining
Volume
DVD
Play
Skip next
C Sw
IR
Kitchen
(Zone 5)
Pantry
Patio
(Zone 6)
IR
C
A
C
Sw
Volume
DVD
Play
Skip next
RJ45
Garage
C
L
BR3
(Zone 3)
IR
Sw
C
IR
C
DA
Sw BR2
(Zone 2)
L
BIR
C
C
A
Sw
IR
BR1
(Zone 1)
L
Light
Radio
DVD
Dyn1
RJ45
RJ45
Vol
TV
Local
Dyn2
Volume
DVD
Play
Skip next
Vol
Src
Dyn1
Dyn2
/
M
A DA
IR
Matrix Switcher, 3×MRA Amps, Source Equipment
MRA Remote Amp, MRA Desktop Amp
Sw
Speaker (wall surface mounted)
L
IR Target (ceiling mounted)
C-Bus Cat-5 cable
IR
C
C-Bus wall switch
Local Input (on wall plate)
IR Target (ceiling mounted)
C-Bus connection point
Figure 7 – C-Bus cabling and termination
13
Multi Room Audio System
Depending on the installation, speakers may be mounted on a wall using brackets, or flush mounted on a wall or ceiling. When speakers are mounted on brackets, it is recommended that an RCA wall plate is installed adjacent to each speaker.
Spring-release or screw binding post wall plates are used to connect to speaker outputs of the Amplifiers.
Use low impedance speaker cable to connect the binding post (Amplifier) wall plates to the RCA (speaker) wall plates. This is especially important with long cable runs.
Figure 8 illustrates how an RCA wall plate is used to connect a speaker.
This is ideal for speakers which have been mounted on walls using
brackets, as in the example installation in Figure 9.
Figure 8 – An RCA wall plate makes a practical speaker connection point
14
Installation Instructions
R
Family
(Zone 4)
IR
RCA
L Sw
R b b b
Dining
L
BR3
(Zone 3)
R
IR
Sw
R
RCA
R
(Zone 6)
IR b
A
R
Sw
IR
Kitchen
(Zone 5)
R
Pantry
Sw
R
Garage
R b
DA
IR
R
Sw BR2
(Zone 2)
L
BIR b A
Sw
R
IR
BR1
(Zone 1)
L
R
RCA
RCA
M
A DA
IR
Matrix Switcher, 3×MRA Amps, Source Equipment
MRA Remote Amp, MRA Desktop Amp
Sw
Speaker (wall surface mounted)
L
IR Target (ceiling mounted) IR
Speaker cable R b
C-Bus wall switch
Local Input (on wall plate)
IR Target (ceiling mounted)
RCA wall plate binding post wall plate
Figure 9 – Speaker cabling and termination
15
Multi Room Audio System
5.5 Digital Audio Cabling
A digital audio cable must be connected between each Amplifier and the
Matrix Switcher. Use Cat-5 Unshielded Twisted Pair (UTP) data cable, and appropriately wired RJ45 plugs and wall plates.
Since Cat-5 cable may be used for several purposes within the same installation, it is recommended you use green cable for digital audio connections, pink for C-Bus and blue for Ethernet. Wall plates should be labelled to differentiate between the various RJ45 connection types.
Colour coding of sockets is recommended.
Avoid laying digital audio cable alongside mains cable, as electromagnetic interference (EMI) can disrupt the signal. An individual Cat-5 cable which connects a digital audio output to an input should not exceed
45 metres. This is illustrated in Figure 10.
POWER
MUTE
45 metres maximum
ZONES
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
45 metres maximum
AUDIO R AUDIO L
DC 24V
INPUT
POWER
IR
DIGITAL
AUDIO
OUTPUT
POWER
MUTE
Figure 10 – Maximum digital audio cable length
16
Installation Instructions
BR3
(Zone 3)
IR
Sw
L
RJ45
Family
(Zone 4)
IR
L Sw
M D
D
D
Dining
Lounge
Patio
(Zone 6)
IR
D
A
Sw
IR
Kitchen
(Zone 5)
Pantry
Sw
RJ45
Garage
IR
D
DA
Sw BR2
(Zone 2)
L
BIR
D A
Sw
IR
BR1
(Zone 1)
L
RJ45
RJ45
M
A DA
IR
Matrix Switcher, 3×MRA Amps, Source Equipment
Sw
MRA Remote Amp, MRA Desktop Amp
Speaker (wall surface mounted)
L
IR Target (ceiling mounted)
Cat-5 cable
IR
D
C-Bus wall switch
Local Input (on wall plate)
IR Target (ceiling mounted)
Digital Audio wall plate
Figure 11 – Digital audio cabling and termination
17
Multi Room Audio System
5.6 IR Target Cabling
An infrared (IR) target can be connected to the green Phoenix socket on the rear of each Amplifier. This allows an IR remote control to operate audio source equipment which is fitted with IR emitters connected to the
Matrix Switcher. Figure 12 shows two methods of connecting an IR target
to an Amplifier.
A suitable IR target is the Clipsal 8050TT Tube Target mounted on a ceiling or wall (optionally via a wall plate). Extend the cable if required and wire to a 3.5 mm stereo socket on a wall plate adjacent to the Amplifier.
Up to 45 m of total cable may be used between a target and the Matrix
Switcher (or Distribution Unit in standalone mode). Create a lead to connect the Amplifier IR input to the 3.5 mm wall plate socket.
A Clipsal 8050ST Shelf Top Target can be mounted on top of a Desktop
Amplifier and plugged directly into the IR input on its rear panel.
IR signals received by external IR targets cannot directly control the Amplifiers. Such control is accomplished via the IR receiver built into the front panel of the Desktop Amplifier. wall plate with
3.5 mm stereo socket
8050ST Shelf
Top IR Target
8050TT Tube IR Target
Connection via a wall plate Direct connection
Figure 12 – Connecting an IR target to an Amplifier
18
Installation Instructions
BR3
(Zone 3)
IR
Sw
L
3.5 mm
Family
(Zone 4)
IR
L Sw
M I
I
I
Dining
Lounge
Patio
(Zone 6)
IR
I
A
Sw
IR
Kitchen
(Zone 5)
Pantry
Sw
3.5 mm
Garage
IR
I
DA
Sw BR2
(Zone 2)
L
BIR
I A
Sw
IR
BR1
(Zone 1)
L
3.5 mm
3.5 mm
M
A DA
IR
Matrix Switcher, 3×MRA Amps, Source Equipment
Sw
MRA Remote Amp, MRA Desktop Amp
Speaker (wall surface mounted)
L
IR Target (ceiling mounted)
IR Target cabling
IR
I
C-Bus wall switch
Local Input (on wall plate)
IR Target (ceiling mounted)
IR Target connection point
(3.5 mm stereo socket)
Figure 13 – IR target cabling and termination
The example installation in Figure 13 uses ceiling mounted Clipsal 8050TT
Tube Targets for Remote and Desktop Amplifiers.
19
Multi Room Audio System
5.7 Shielded Audio Cabling
Multi Room Audio Amplifiers have line level local audio inputs (LOCAL IN), which can be used to play audio from a locally connected music player or
PC. Amplifiers also have volume affected line level audio outputs (ZONE
OUT) which can be connected to other audio equipment. The Desktop
Amplifier has a headphone output. These inputs and outputs should be cabled and terminated if they are to be utilised.
It is recommended that wall plates with appropriate audio sockets be used to provide input and output connection points to the Amplifier. Use RCA sockets at the Amplifier end for local inputs and line outputs. Use 3.5 mm stereo sockets at the other end to provide the connection points for external audio equipment. Use 3.5 mm stereo sockets for headphone connections.
When installing audio cable:
• wire wall plates with suitably shielded stereo audio cable
• avoid laying audio cable alongside mains cable to minimise EMI pickup
• do not earth audio ground terminals.
Cabling and wall plate requirements for the example installation are
20
Installation Instructions
BR3
(Zone 3)
IR
Sw
L
L
RCA
Lounge
Family
(Zone 4)
IR
3.5 mm
L
L
Sw
M
R
R
Dining
Patio
(Zone 6)
IR
A
Garage
Sw
IR
Kitchen
(Zone 5)
Pantry
Sw
IR
R
DA
Sw BR2
(Zone 2)
L
H
BIR
R A
Sw
IR
BR1
(Zone 1)
L L
RCA +
3.5 mm
3.5 mm
RCA
3.5 mm
M
A DA
IR
H
Matrix Switcher, 3×MRA Amps, Source Equipment
MRA Remote Amp, MRA Desktop Amp
Sw
Speaker (wall surface mounted)
L
IR Target (ceiling mounted)
Speaker cable
Headphone + Local audio input wall plate
(3.5 mm stereo socket)
IR
R
L
C-Bus wall switch
Local Input (on wall plate)
IR Target (ceiling mounted)
RCA wall plate
Local audio input wall plate
(3.5 mm stereo socket)
Figure 14 – Shielded audio (local input/headphone output) cabling & termination
21
Multi Room Audio System
5.8 Connecting Multi Room Audio Units
Once wall plate connections have been installed and cabled and speakers have been connected, you are ready to connect the Multi Room Audio
Amplifiers and Matrix Switcher.
Figures 15 to 17 show the connection of Amplifiers for zones 1, 2 and 6 of
the example system. Figure 18 shows the connection of Amplifiers for
zones 3, 4 and 5 (which are centrally located), and for the Matrix Switcher.
Unit connections are identified on Page 53. Descriptions of the front
panels are provided in the Amplifier and Matrix Switcher User’s Guides.
Zone 1 Remote Amp (BR1)
L R
DIGITAL
AUDIO IN
ZONE
OUT L
LOCAL
IN
EXTERNAL
IR OPTICAL
POWER TARGET IN DIGITAL
AUDIO OUT
R
Unit
Speakers - Zone 1
Local Input
Z1
Figure 15 – Zone 1 Amplifier connections
IR
Z1
Digital
Audio
Z1
C-Bus
22
Zone 2 Desktop Amp (BR2)
L R
DIGITAL
AUDIO IN
ZONE
OUT
L
LOCAL
IN
EXTERNAL
IR OPTICAL
POWER TARGET IN DIGITAL
AUDIO OUT
R
Unit
Installation Instructions
Speakers - Zone 2 IR
Z2
Digital
Audio
Z2
Local Input C-Bus
Z2
Figure 16 – Zone 2 Desktop Amplifer connections
Zone 6 Remote Amp (Patio/Garage)
L R
DIGITAL
AUDIO IN
ZONE
OUT
L
LOCAL
IN
EXTERNAL
IR
POWER TARGET
OPTICAL
IN DIGITAL
AUDIO OUT
R
Unit
Speakers - Zone 6 IR
Z6
Digital
Audio
Z6
C-Bus
Figure 17 – Zone 6 Amplifier connections
23
Multi Room Audio System
L R
EXTERNAL
IR OPTICAL
POWER TARGET IN DIGITAL
AUDIO OUT
ZONE
OUT L
LOCAL
IN
R
Unit
Zone 5 Amp
(Kitchen)
L R
DIGITAL
AUDIO IN
ZONE
OUT
L
LOCAL
IN
EXTERNAL
IR OPTICAL
POWER TARGET IN DIGITAL
AUDIO OUT
R
Unit
Zone 4 Amp
(Family)
L R
DIGITAL
AUDIO IN
ZONE
OUT L
LOCAL
IN
EXTERNAL
IR OPTICAL
POWER TARGET IN DIGITAL
AUDIO OUT
R
Unit
Zone 3 Amp
(BR3)
Speakers - Zone 5
Speakers - Zone 4
IR
Z5 Z4 Z3
C-Bus
Local Inputs
Z3
Z4
Speakers - Zone 3 Digital Audio
Z6 Z2 Z1
Only use F 3,15A L 250V fuse
1 IR OUT 2
DIGITAL AUDIO OUT
CAUTION: USE ONLY WITH C-Bus MULTIROOM AUDIO SYSTEM AMPLIFIERS
ZONE 8 ZONE 7 ZONE 6 ZONE 5 ZONE 4 ZONE 3 ZONE 2 ZONE 1
OUT
OPTICAL
IN
DIGITAL
AUDIO
IN
1
SOURCE INPUT
2 3 4 L
BROADCAST
USB
R
C-Bus
Unit
To IR Emitters on source equipment
To optical output on source equip.
To Distribution Unit output (provides an extra stereo input)
To audio line outputs on source equipment
Figure 18 – Matrix Switcher and Zone 3 to 5 Amplifier connections
24
Installation Instructions
6.0 C-Bus System Clock
The Multi Room Audio Matrix Switcher and Amplifiers incorporate a software selectable C-Bus system clock. The system clock is used to synchronise data communication over a C-Bus network. At least one active
C-Bus system clock is required on each C-Bus network for successful communication. No more than three units on any C-Bus network should have clock circuitry enabled, so this option is normally disabled using the
C-Bus Toolkit software.
If a system clock is required, it can be enabled when editing the unit in the
C-Bus Toolkit software.
The Multi Room Audio Matrix Switcher and Amplifiers incorporate a software selectable network burden. The network burden can be enabled when editing the unit in the C-Bus Toolkit software, but only if the C-Bus system clock is also enabled.
One network burden is normally required to ensure correct operation of each C-Bus network. The Network window of a C-Bus Toolkit project provides a summary of a C-Bus network according to the units added to the Database. This can be helpful in determining how many burdens are required on a particular network.
25
Multi Room Audio System
8.0 C-Bus Power Requirements
The Matrix Switcher has a built-in C-Bus Power Supply which provides
330 mA to the C-Bus network. Multi Room Audio Amplifiers draw 22 mA from the C-Bus network.
The Matrix Switcher supplies enough C-Bus power for at least seven Multi
Room Audio Amplifiers and seven C-Bus wall switches (such as the Ulti
Saturn or DLT).
The Distribution Unit does not connect to C-Bus and therefore does not impact on the power requirements of a C-Bus network.
The Network window of a C-Bus Toolkit project provides a summary of a
C-Bus network according to the units added to the Database. This can be helpful in determining the power supply requirements of a particular network.
External power surge protection devices should be used to enhance system immunity to power surges. It is strongly recommended that overvoltage protection equipment such as the Clipsal 970 Series be installed at the switchboard.
26
Installation Instructions
10.0 Programming and Setup
Once a Multi Room Audio (MRA) system has been installed, it must be configured using the C-Bus Toolkit software and the Multi Room Audio
Rapid Programming Application (MARPA).
Radio Tuner
(Audio source #1)
DVD
(Audio source #3)
Infrared
Analogue Audio
Digital Audio
C-Bus
Digital TV
(Audio source #2) Unit
C-Bus
1 2 3 4
Dimmer
IR
Target
ZONES
1 2 3
IR
Target
4 5 6 7 8
IR
Target
Computer
(Local Input)
POWER
MUTE
Computer
(Local Input)
Volume
Radio
Station+
Station-
14:02
2
Volume
Nxt Srce
Dyn. Ctrl 1
Dyn. Ctrl 2
Vol. Up
Vol. Dn
Radio
Nxt Srce
Light
Radio
DVD
Dyn. Ctrl 1
Dyn. Ctrl 2
Zone 1 Zone 2
Figure 19 – Example system to be configured by software
Zone 3
Volume
TV
Local
27
Multi Room Audio System
It is highly recommended that you complete a C-Bus Training Course before configuring a Clipsal Multi Room Audio system. Sections 10.1 and
10.2 take you through the configuration process. These sections assume you are familiar with the C-Bus Toolkit software. They use the example
system shown in Figure 19. This system consists of three zones and uses
the following units (all on the same C-Bus network):
1 × Matrix Switcher
2 × Remote Amplifiers
1 × Desktop Amplifier
1 × Ulti Saturn DLT wall switch
1 × 6 button Ulti Saturn wall switch
1 × 8 button Neo wall switch
1 × radio tuner (audio source #1)
1 × digital TV set top box (audio source #2)
1 × DVD player (audio source #3)
1 × 4 Channel Dimmer.
C-Bus programming is accomplished using the C-Bus Toolkit software. It involves:
• creating a C-Bus project with a Group Address structure which is used by MRA Amplifiers and the MARPA software
• enabling a C-Bus system clock and burden in the Matrix Switcher
(if required)
• configuring each MRA Amplifier so it can be controlled by one or more C-Bus wall switches.
1) Start Toolkit, and create a new C-Bus project and network for the
MRA system. If a project and network already exist (such as when you are adding to an existing C-Bus network), open that project and network.
2) Decide which Application you will use for the MRA system. You may create a unique Application (such as “Lighting/Audio” Application
Address 55). However, if you use C-Bus wall switches to control both lights and audio, both need to use the same Application Address. In this case it may be best to use the default “Lighting” Application
Address 56.
28
Installation Instructions
3) Create the Group Addresses. These are used to associate buttons on wall switches or a touch screen with Amplifier control functions such as volume and source selection. For each Amplifier, create a Group
Address for each of the following that will be controlled from a C-Bus device:
• Absolute Source (used in combination with a selector)
It is suggested you use clearly identifiable tag names/descriptions when you create the Group Addresses. Suitable Groups for the example MRA
system in Figure 19 are shown in Figure 20.
Figure 20 – Group Addresses used in the example MRA system
29
Multi Room Audio System
4) A button on a wall switch can be used to select a specific audio source (absolute source). This is normally achieved by configuring the button as a scene. If you program a C-Bus DLT wall switch to select an absolute source, you must create a Group Address in the Trigger
Control Application and an Action Selector (selector) for each scene.
These allow you to send labels to the DLT scenes. Such a Trigger
Control Group Address with selectors is shown in Figure 21.
Figure 21 – Selectors used in DLT scenes for absolute source selection
5) Two dynamic control buttons can be used on a wall switch to perform different functions depending on which source is selected. If you use dynamic control buttons you must create a Group Address in the
Trigger Control Application and a selector for each function. These selectors are used when configuring the Matrix Switcher with the
MARPA software. A Trigger Control Group Address with selectors
used in the example MRA system is shown in Figure 22.
Figure 22 – Selectors used for the dynamic control functions
30
Installation Instructions
6) Select the Units branch of the C-Bus Toolkit tree view and add the
C-Bus units to the network. Figure 23 shows C-Bus Toolkit after
adding the units used in the example MRA system. Added units consist of:
1 × MRA Matrix Switcher
3 × MRA Amplifiers
3 × C-Bus wall switches
1 × DIN Rail Dimmer.
Figure 23 – Units added to the network in the MRA project
7) Configure the Matrix Switcher unit (if necessary). The Matrix Switcher needs to be configured in Toolkit only to enable its C-Bus system clock or network burden. In a C-Bus network consisting entirely of
MRA devices, or where the Matrix Switcher is the only unit with a
C-Bus power supply, it is recommended that you enable the Matrix
Switcher’s C-Bus system clock and burden. This is shown in Figure 24.
Figure 24 – Enable the Matrix Switcher's C-Bus clock and burden
31
Multi Room Audio System
8) Configure the Amplifiers. In a typical MRA system such as in Figure 19
the default settings on the Audio Levels and Zoning tabs are sufficient. The Remote tab (Desktop Amplifier) is configured by default to use the remote control supplied with the Desktop Amplifier.
The C-Bus Control tab must be configured in order to control an
Amplifier from a C-Bus wall switch. Select the Application first. Then specify which Group Addresses will be used to control the Volume,
Bass and Treble, the Next, Previous and Absolute Sources, and the
Dynamic controls. Use the Group Addresses you created in Step 3.
Figures 25 to 27 show the configurations for the Amplifiers in the example MRA system.
Figure 25 – The C-Bus Control tab for the Zone 1 Remote Amplifier
Figure 26 – The C-Bus Control tab for the Zone 2 Desktop Amplifier
32
Installation Instructions
Figure 27 – The C-Bus Control tab for the Zone 3 Remote Amplifier
The Absolute source is used to select a specific audio source, such as Analogue Source 1 or Local Input. It consists of a Group
Address and a selector (level). When selecting an Absolute Group
Address, you are asked if you want to create levels for the selected Group Address. After responding with Yes, you can click the Parameters button to see which levels are used to select
specific audio sources. This is shown in Figure 26. The same levels
are always used for the respective sources.
9) Configure the wall switches. For most control functions you simply select the Group Address and function type. It is recommended you use the following functions:
• Bell Press for Next and Previous Source
• On/Off for Dynamic control
• Scene for Absolute Source selection
• Dimmer for a single Volume button, Dimmer Down/Dimmer Up for a pair of Volume buttons
• Dimmer for a single, or Dimmer Down/Dimmer Up for a pair of
Bass or Treble buttons. Use a short release recall level of 50% so that a quick-press sets the bass or treble to mid range. Do
this via the Key Function and Blocks tabs (refer to Figure 28).
33
Multi Room Audio System
Button 1 used for single button bass or treble
Buttons 2 and 3 used for bass or treble pair
Set Short Release to
Recall 1 (or Recall 2)
Key Functions tab
Set Recall 1 (or Recall 2) level to 50%
Blocks tab
Figure 28 – Setting short release recall levels for bass and treble buttons
Figure 29 shows configuration of the C-Bus DLT wall switch used in
Zone 1 of the MRA example system.
Figure 29 – Configuring the C-Bus DLT wall switch for Zone 1
34
Installation Instructions
Absolute Source selection is a little more complicated, as it is best performed using a scene. To configure a button that selects an absolute source using a scene:
i) Select the Scene function for the button. (Note that a button is referred to as a key in some versions of Toolkit). up the “Define a Scene” panel. If you are using a C-Bus DLT wall switch, you must select a Trigger Group and Trigger Group
Action Selector on this panel so you can send labels to the DLT later. Use the Group Address and selector(s) you created in
Step 4. An example is provided in Figure 30.
iii) Click the Edit Scenes button to bring up the Scene Manager.
Select the Group Address used for Absolute Source selection
(from the list on the right hand side), and click the “<” button to add it to the list of Commands. Type the level which corresponds to the relevant source, in the box next to the
slider. Absolute source levels can be seen in Figure 26.
Figures 31 and 32 show the configuration of the Ulti Saturn wall switch used in Zone 2 of the MRA example system.
Figure 30 – Defining a scene on a DLT
35
Multi Room Audio System
Figure 31 – Configuring the Ulti Saturn wall switch for Zone 2
If a wall switch is programmed with one or more absolute source buttons as well as a next/previous source button, add the next/previous source Group Address(es) to the scene used for absolute source selection. This will force the scene button’s indicator to switch off when the next or previous source button is
selected. This is shown in Figure 32.
36
Installation Instructions
Figure 32 – Configuring a button for absolute source selection for Zone 2
37
Multi Room Audio System
Figures 33 to 36 show the configuration of the Neo wall switch used in Zone 3 of the MRA example system.
Figure 33 – Configuring the Neo wall switch for Zone 3 (showing Scene 1)
38
Installation Instructions
Figure 34 – Configuring the Neo wall switch for Zone 3 (showing Scene 2)
39
Multi Room Audio System
Figure 35 – Configuring the Neo wall switch for Zone 3 (showing Scene 3)
40
Installation Instructions
Figure 36 – Configuring the Neo wall switch for Zone 3 (showing Scene 4)
41
Multi Room Audio System
9) Configure any additional C-Bus units. Figure 37 shows the config-
uration of the 4 Channel Dimmer used in the example MRA system.
Figure 37 – Configuring the 4 Channel Dimmer in the example MRA system
10) Connect your PC to the C-Bus network in the usual way and open the network (right click on the Network branch in the tree and select
Open Network). Scan the units in from the live network (click the
Units branch of the tree and then click the Scan Network button).
Use the “All -> Network” button to transfer the information from the units in the database to the units on the C-Bus network.
Multiple Amplifiers in the Same Zone
You can connect multiple Amplifiers to the same zone. The Digital Input of the first Amplifier in the zone is connected to the Digital Output of the
Matrix Switcher (or Distribution Unit). The Digital Output of the first
Amplifier is connected to the Digital Input of the next Amplifier and so on, so that each Amplifier is connected to the previous in series.
When configuring Amplifiers connected in this way, set one Amplifier as a
Master and all others as Slaves (on the Audio Levels tab). It is recommended you set a Desktop Amplifier as the Master if the zone includes any
Amplifiers of this type.
42
Installation Instructions
Amplifiers in Standalone Mode
When Amplifiers are connected in standalone mode (using a Distribution
Unit instead of a Matrix Switcher), the zone number must be manually configured for each Amplifier. This is done on the Zoning tab, shown in
For the Amplifiers used in the standalone configuration in Figure 3
(Page 8), the first Amplifier would be set to Zone 1, the second to Zone 2
and the third to Zone 3. All Amplifiers connected in the same standalone installation must be set to the same Matrix Switcher number.
Figure 38 – Setting the zone number of a standalone Amplifier
43
Multi Room Audio System
10.2 MARPA
The Matrix Switcher needs to be programmed with the Multi Room Audio
Rapid Programming Application (MARPA). Use this application to:
• assign an ID to the Matrix Switcher (in case multiple Matrix
Switchers are used on the same network of a C-Bus installation)
• configure parameters for each audio source, such as,
– the label (description) displayed when the source is selected
– whether the source is available
– which C-Bus commands are triggered by the Dynamic controls
• configure parameters for each zone, including,
– the label (description) displayed when the zone is selected
– whether labels are sent to C-Bus DLT switches
– whether the local input source is available
• configure IR maps for dynamic control (if used).
1)
Start MARPA and choose the Create New Project action (Figure 39).
Figure 39 – The MARPA start-up window
44
Installation Instructions
2) Select the C-Bus project you created in Toolkit, then select the
network (Figure 40). Click OK.
Figure 40 – Selecting the C-Bus project and network
3) The General branch of the Project tree is selected. The default settings on this branch are suitable for a typical single Matrix
Switcher system such as the example MRA system. If you have multiple Matrix Switchers on the same C-Bus network (you can have up to three), you need to give each one a unique number.
Figure 41 – MARPA's General branch
45
Multi Room Audio System
4) Select the Sources branch of the Project tree. The Local source tab is
selected (Figure 42). The Description of the Local source can be
changed here. Its default is “Local”. The Description is displayed on the Matrix Switcher LCD when the source is selected. It is also displayed as the label for the source selection control group on a
C-Bus DLT wall switch if DLT labelling is enabled.
Figure 42 – The Local tab of MARPA's Sources branch
5) In turn, select each of the six distributable sources (Analogue 1 to
Optical), and:
• disable the “Include this source in “Next” and “Previous” navigation cycle” checkbox if the source will be unused
• enter the Description (if the source will be used)
• enter the Description for the Dynamic 1 and 2 controls (if used)
• select the Trigger Group and Selector for the Dynamic 1 and
Dynamic 2 control (if used).
The Analogue 1, 2 and 3 tabs shown in Figures 43 to 45 are
configured for the example MRA system shown in Figure 19. Since
the Analogue 4, Digital and Optical source inputs are not used in the example system, the “Include this source in “Next” and “Previous” navigation cycle” checkbox is disabled in their respective tabs, as
46
Installation Instructions
Figure 43 – The Analogue 1 tab configured for the example MRA system
Figure 44 – The Analogue 2 tab configured for the example MRA system
47
Multi Room Audio System
Figure 45 – The Analogue 3 tab configured for the example MRA system
Figure 46 – The Analogue 4 tab configured for an unused source
48
Installation Instructions
6) Select the Zones branch of the Project tree. Select each Zone tab that corresponds to a zone used in the MRA system. On each:
• enable the “Generate DLT Labels” checkbox if any C-Bus DLT switches exist in the zone
• enable the Local Source checkbox if a local input may be used in an Amplifier in the zone
• enter the Description (displayed on the Matrix Switcher LCD when a zone selection button is pressed).
Figures 47 and 48 show the Zone 1 and Zone 2 tabs configured for
the example MRA system shown in Figure 19. Since a C-Bus DLT wall
switch exists in zone 1 only, the Zone 1 tab has its “Generate DLT
Labels” checkbox is enabled, but the Zone 2 tab does not.
Figure 47 – The Zone 1 tab configured for the example MRA system
Figure 48 – The Zone 2 tab configured for the example MRA system
49
Multi Room Audio System
Mapping IR Codes to the Dynamic Controls
It is recommended you import the IR codes specific to the devices you will be controlling. IR codes can be obtained using the Clipsal IR Code Learning
Unit (Catalogue Number 5100RP) and the IR Reader Software. Together these products learn the codes from an Infrared Control and output them in XML format.
7) Select the User branch of the IR Library tree. Unless the device is already present in the list, click the Import button and select and open the IR Reader file to be imported. Select the device in the list (if
not already selected) and click the Add to Project button. Figure 49
shows an example device selected in the User branch of the IR
Library.
Figure 49 – A device selected in the User branch of the IR Library
8) Select the C-Bus IR Maps branch of the Project tree. This is where you map the IR codes to selectors in Trigger Control Group Addresses.
i) Click the Add button to bring up the “Add C-Bus IR Map to
Project” panel.
ii) In the left hand window, click on the [+] next to the Trigger
Control branch to expand the tree. iii) Click on the [+] next to the Dynamic_Control group you created in Toolkit, to reveal the selectors. iv) In the right hand window, expand the IR code tree to reveal the commands.
v) For each selector on the left, click the IR command on the right and while continuing to hold down the mouse, drag the command across to the selector.
50
Installation Instructions
Figure 50 shows how to map a remote command to a selector used
for dynamic control. After dropping a remote command on a selector, you are prompted to select which channel or channels the IR command is to be output on. These are the physical “IR Out” emitter connectors on the rear of the Matrix Switcher. hold down the mouse button and drag across to the selector
Click the IR command
Choose which
Matrix Switcher
IR Out channel to use
Figure 50 – Mapping IR codes to Dynamic controls
9)
Click the Save button (Figure 51) to save the MARPA project.
IR codes have been added
Figure 51 – Buttons on the MARPA tool bar
51
Multi Room Audio System
10) Transfer the project to the Matrix Switcher. To do this:
i) Ensure power is connected to the Matrix Switcher and the unit is switched on. A power switch is located on the rear of the
Matrix Switcher, next to the AC power socket.
ii) Use the supplied USB cable (1 m Type A to Type B). Do not extend its length or substitute it for a longer cable. Plug one end into your PC and the other into the rear of the Matrix
Switcher. iii) Wait about 30 seconds for the driver to respond. If this is the first time you have connected the Matrix Switcher to your PC via the USB, and depending on which operating system you are using, you may be prompted to install driver software (“Found
New Hardware”). If so, proceed with the recommended automatic option.
iv) Click the “Transfer to Unit” button in MARPA (Figure 51).
v) Select the COM port used by the USB cable. This is likely to be the one with the highest number. vi) Click the Start button. A progress bar is displayed as the project
is transferred (Figure 52). The project may take one or two
minutes to transfer. If a Communications Failure message is displayed, select a different COM port and try again.
Figure 52 – A progress bar is displayed as the project is transferred
52
Installation Instructions
11.0 Unit Connections
Power
Supply input analogue audio inputs
AUDIO R AUDIO L
IR emitter output
IR
DIGITAL
AUDIO
OUTPUT
DC 24V
INPUT
POWER power indicator digital audio output
Note:
When connecting a Distribution Unit to an Amplifier which has a Power
Supply (PS) connected, it is not necessary to connect a PS to the
Distribution Unit.
Figure 53 – Distribution Unit connections and indicator
Connection
/Indicator
Description
Analogue audio inputs
Power Supply input
The line level stereo analogue audio connection.
IR emitter output This 3.5 mm socket connects to an IR Emitter Lead.
IR Emitters can be coupled to IR receivers on equipment, providing remote control from any zone through the Multi Room Audio system.
The 24 V DC Distribution Unit Power Supply connection. This is used when connecting the
Distribution Unit to a Matrix Switcher. The Power
Supply not required when the digital audio output is connected to the digital audio input of an Amplifier.
53
Multi Room Audio System
Connection
/Indicator
Description
Power indicator Indicates that power is connected to the unit.
Digital Audio
Output
This RJ45 connection outputs the digital audio which has been converted from the analogue input.
This connects to a digital input on the Matrix
Switcher or Amplifier.
11.2 Amplifiers
Digital audio (zone) input
Speaker outputs
Zone outputs
Local inputs
Headphone output
L R
DIGITAL
AUDIO IN
ZONE
OUT
L
LOCAL
IN
C-Bus
EXTERNAL
Unit
IR OPTICAL
POWER TARGET IN DIGITAL
AUDIO OUT
R
C-Bus indicators
External power input
Infrared input
Digital audio output
Digital optical input
Figure 54 – Desktop Amplifier rear panel connections and indicators
54
Installation Instructions
Digital audio (zone) input
Speaker outputs
Zone outputs
Local inputs
L R
DIGITAL
AUDIO IN
ZONE
OUT
L
LOCAL
IN
EXTERNAL
IR OPTICAL
POWER TARGET IN DIGITAL
AUDIO OUT
R
Unit
Power LED
C-Bus
C-Bus indicators
External power input
Infrared input
Digital audio output
Digital optical input
Figure 55 – Remote Amplifier rear panel connections and indicators
Connection
/Indicator
Description
Speaker outputs These are used to connect to 4 Ω to 8 Ω speakers which are rated at 25 W RMS @ 4 Ω (or 6 W RMS @
4 Ω if no external power supply is connected to the
Amplifier).
Digital audio
(zone) input
The zone output of the Matrix Switcher is connected to this input. Alternatively a Multi Room Audio
Distribution Unit can be connected to this input, providing one stereo audio input. In this mode, the
Amplifier can select between two audio sources:
Digital audio input and local input.
Zone outputs
(1 × RCA pair)
Local inputs
(1 × RCA pair)
These are line level outputs of the selected audio source as received by the Amplifier. The outputs are affected by the volume, bass and treble settings of the Amplifier.
Use this to Connect a local analogue audio source which is available to this Amplifier only.
55
Multi Room Audio System
Connection
/Indicator
External power input
Infrared input
Digital optical input
Digital audio output
C-Bus (×2)
C-Bus indicators
Description
This provides power to the Amplifier (when a Matrix
Switcher is not used). An external power supply also increases the Amplifier’s audio output capacity to
25 W RMS into 4 ohm speakers.
Power supply rating: 24 V DC, 3.75 A or 21 V AC, 3.5 A.
This Phoenix socket connects to an IR Target, allowing an infrared
GND remote to control
Signal equipment located near
+12 V the Matrix Switcher.
Use this to connect a digital optical audio source to the Amplifier instead of the digital audio (zone) source. The digital audio format must be 44.1 or 48 kHz stereo. Some digital audio formats (such as surround sound) are not compatible with the
Amplifier. Either a digital audio (zone) or digital optical audio source may be connected to the
Amplifier, but not both simultaneously.
This is used to connect an additional Amplifier to the same zone as this Amplifier. A Cat-5 cable is used to connect to the additional Amplifier’s Digital audio
(zone) input. Both Amplifiers will use the same zone
(they will both select the same audio source).
Connects to the C-Bus network.
Unit
On: C-Bus network connected
Flashing: Data exchange in progress
C-Bus
On:
Off:
C-Bus network operational
Insufficient C-Bus power or clock
Flashing: Insufficient C-Bus power
Table 2 – Amplifier connectors and indicators
56
Installation Instructions
Power switch
AC power input
Infrared outputs
Mono broadcast inputs
USB
C-Bus
Only use F 3,15A L 250V fuse
1 IR OUT 2 DIGITAL AUDIO OUT
ZONE 8
CAUTION: USE ONLY WITH C-Bus MULTIROOM AUDIO SYSTEM AMPLIFIERS
ZONE 7 ZONE 6 ZONE 5 ZONE 4 ZONE 3 ZONE 2 ZONE 1
OUT
OPTICAL
IN
DIGITAL
AUDIO
IN
1
SOURCE INPUT
2 3 4 L
BROADCAST
USB
R
C-Bus
Unit
Digital optical output
Digital optical input
Digital zone outputs
Digital audio input
Stereo analogue inputs
C-Bus indicators
Mono level adjustment
Figure 56 – Matrix Switcher rear panel connections and indicators
Connection
/Indicator
Power switch
Mains power input (IEC)
Infrared outputs
(×2)
Description
Switches the mains power input on and off.
Connect mains here to power the Matrix Switcher, and any connected Multi Room Audio Amplifiers which do not have an external power supply.
Use these 3.5 mm sockets to connect to IR Emitter
Leads. IR Emitters can be coupled to IR receivers on equipment, providing remote control from any zone through the Multi Room Audio system.
57
Multi Room Audio System
Connection
/Indicator
Mono broadcast inputs (×2)
USB (Type B)
C-Bus (×2)
Digital optical output
Digital optical input
Digital zone outputs (×8)
Digital audio input
Description
Line level mono audio connected here is broadcast to all zones which have an analogue input source selected.
There are two mono inputs with different priorities.
Audio connected to the Lo input is transmitted by
Amplifiers at their current level.
Audio connected to the Hi input is transmitted at a preset level. Amplifiers which have a digital input source selected, change to the fourth analogue source so they can receive the high priority broadcast audio.
Note: High priority (HI) broadcast audio uses left channel speakers. Low priority (LO) broadcast audio uses right channel speakers.
This is used by the installer to configure the Matrix
Switcher.
Connects to the C-Bus network.
Retransmits the data received by the digital optical input.
Use this to connect a digital optical audio source to be distributed to any of the eight zones. The digital audio format must be 44.1 or 48 kHz stereo. Some digital audio formats (such as surround sound) are not compatible with the Matrix Switcher.
Each zone output is used to connect the Matrix
Switcher to one Amplifier in each zone. Additional
Amplifiers can be added to a zone by connecting their Digital Audio In socket to the Digital Audio
Out of an existing Amplifier.
A Multi Room Audio Distribution Unit can be connected to this input, providing an additional stereo audio input.
58
Installation Instructions
Connection
/Indicator
Stereo analogue inputs
(4× RCA pairs)
Mono level adjustment (×2)
C-Bus indicators
Description
Connect up to four stereo analogue inputs to be distributed to any of the eight zones.
These adjust the level of the audio source connected to the mono broadcast inputs. Use a small flat head screwdriver to rotate the control if the audio source is too quiet or loud.
Unit
On: C-Bus network connected
Flashing: Data exchange in progress
C-Bus
On: C-Bus network operational
Off: Insufficient C-Bus power or clock
Flashing: Insufficient C-Bus power
Table 3 – Matrix Switcher connectors and indicators
59
Multi Room Audio System
12.0 Troubleshooting
Symptom
There is no sound after switching the Amplifier on
(sound worked previously).
Possible Explanation
The volume may have been set to minimum, or the Amplifier may have been Muted (on a Desktop Amplifier) before the Amplifier was switched off.
The default volume, bass or treble settings have changed
(when switching the Amplifier on).
A mains circuit breaker trips when Amplifiers are powered up.
Unexpected behaviour occurs after the digital zone connections are changed.
The wrong Amplifier is responding to source changes.
The Matrix Switcher no longer responds to button presses.
If a power failure occurs when the
Amplifier is on, the volume, bass and treble settings are saved and become the new defaults.
This may occur if more than five
Amplifier power supplies are connected to the same circuit, due to a high inrush current.
The Amplifier’s zone settings are not reset until all power is removed from the Amplifier. Alternatively use the
Reset Amplifier function on the unit’s
C-Bus Status tab in the C-Bus Toolkit software.
The “Use Matrix Switcher auto assigned zone” option may not be enabled. This option is in the Amplifier’s Zoning tab in the C-Bus Toolkit software. After changing the status of this option (on a live network), use the Reset Amplifier function on the C-Bus Status tab.
Switch the Matrix Switcher off for several seconds, then on. Use the power switch on the rear of the Matrix
Switcher, next to the AC power socket.
60
Installation Instructions
Symptom
Dynamic labels don’t work on a C-Bus DLT wall switch.
Possible Explanation
There are several options which need to be selected for labels to function.
These options are located:
• on the More panel accessed by clicking the “More....” button on the Amplifier’s C-Bus Control tab in
Toolkit
• on the DLT wall switch’s Global tab in Toolkit
• on the Zones branch of the Project tree in the MARPA software.
An Amplifier switches off, particularly when the volume is loud.
An Amplifier emits a high pitched screeching sound when a particular source is selected.
The Matrix Switcher does not power up.
Audio is not broadcast via the
Matrix Switcher’s high priority
(HI) broadcast input.
Cannot hear any sound when using the optical input
If insufficient current is available for the
Amplifier, it will switch itself off. This may occur if the Amplifier receives its power from a Matrix Switcher. The
Amplifier may need its own external power supply unit.
This may occur if an output of an
Amplifier is connected to the input of the Matrix Switcher. Such a connection should be avoided as it can cause a feedback loop.
The fuse may need replacing. Fuse replacement is described in the Matrix
Switcher User’s Guide.
The level of the audio connected to the broadcast input may not be sufficient to trigger the broadcast.
The digital audio source may be connected to the optical output instead of the input (on a Matrix Switcher).
Some digital audio formats (such as surround sound) are incompatible with the MRA system.
61
Multi Room Audio System
13.0 Electrical Specifications
Parameter
Supply voltage
Analogue input signal level
(Audio inputs)
A/D conversion
Operating temperature
Operating humidity
Description
27 V DC (powered by Amplifier via digital audio connection), or
24 V DC @ 500 mA (via external power pack)
2.8 V p-p maximum (31 k Ω)
16 bit PCM
10 to 40 °C (50 to 104 °F)
10 to 90% RH (non-condensing)
Parameter
Supply voltage
Mains frequency range
AC input impedance
Description
240 V AC
47 to 53 Hz and 57 to 63 Hz
47 k Ω
200 W maximum
36 V DC maximum
Power consumption
C-Bus output voltage
C-Bus output current < 330 mA
Network clock and burden Software selectable
Analogue input signal level
(Source inputs)
2.8 V p-p maximum (47 k Ω)
A/D conversion
Operating temperature
16 bit PCM
10 to 40 °C (50 to 104 °F)
Operating humidity 10 to 90% RH (non-condensing)
62
Installation Instructions
13.3 Amplifiers
Parameter
Supply Voltage
C-Bus supply voltage
Power consumption 90 W maximum
Network clock and burden Software selectable
Analogue input signal level
(Local inputs)
2.8 V p-p maximum (47 k Ω)
Maximum power output
D/A conversion
28 W RMS into 4 Ω (0.514% THD)
16 bit PCM
Frequency response
Total harmonic distortion
(1 kHz, 20 W RMS into 4 Ω)
Signal to noise ratio
Operating temperature
Description
27 V DC (powered by Matrix Switcher via digital audio connection), and/or
24 V DC @ 3.75 A (via external switch mode power supply) or 21 V AC @ 3.5 A
(via external linear power supply)
15 to 36 V DC @ 22 mA
40 Hz to 20 kHz (±1 dB)
0.36% (using analogue input )
> 67 db (peak, unweighted)
Desktop Amp.
:
10 to 40 °C (50 to 104 °F)
Remote Amp.
:
10 to 70 °C (50 to 158 °F)
10 to 90% RH (non-condensing) Operating humidity
63
Multi Room Audio System
13.4 System Audio Performance
Parameter
Frequency response
Description
Matrix Switcher
+ Amplifier*
40 Hz to 20 kHz
(+2.4/–0.75 db)
Distribution Unit
+ Amplifier*
†
40 Hz to 20 kHz
(±2.3 dB)
Total harmonic distortion
(1 kHz, 20 W RMS into 4 Ω)
0.16% 0.20%
Signal to noise ratio > 63 dB
(peak, unweighted)
> 63 dB
(peak, unweighted)
* Analogue inputs of Matrix Switcher/Distrib. Unit, measured from Amplifier speaker outputs
†
Amplifier powered by an external switch mode power supply
64
Installation Instructions
14.0 Mechanical Specifications
Unit
Distribution Unit
Desktop Amplifier
Remote Amplifier
Matrix Switcher
Distribution Unit
Weight
180 g
165.5 mm
AUDIO R AUDIO L
IR
DIGITAL
AUDIO
OUTPUT
DC 24V
INPUT
POWER
142.5 mm
50 mm
30.5 mm
65
Multi Room Audio System
Desktop Amplifier
21.5 mm
194.0 mm
8.0 mm
66.1 mm
180.4
mm
105.0
mm
143.0 mm
30.0 mm
66
Installation Instructions
Remote Amplifier
28.6 mm
180.0 mm
2.9 mm 8.0 mm
62.8 mm
175.0
mm
105.0
mm
143.0 mm
30.0 mm
67
Multi Room Audio System
Matrix Switcher
8.3 mm
280.0 mm
8.0 mm
66.1 mm
424.3
mm
346.3
mm
68
228.9 mm
30.0 mm
Installation Instructions
15.0 Standards Complied
DECLARATIONS OF CONFORMITY
Australian/New Zealand EMC & Electrical Safety Frameworks and Standards
The Multi Room Audio Matrix Switcher complies with the following:
Regulation Standard Title
Electrical Safety AS/NZS 60065 Audio, video and similar electronic apparatus - Safety requirements
EMC (C-Tick) AS/NZS CISPR 22 Information technology equipment - Radio disturbance characteristics (emissions)
The Multi Room Audio Amplifiers comply with the following:
Regulation Standard Title
Electrical Safety
(When powered by
AS/NZS 60065 Audio, video and similar electronic apparatus - Safety
PAC090M Power
Supply*) requirements
EMC
(When powered from Matrix switcher or
PAC090M Power
Supply*)
AS/NZS CISPR 13 Sound and television broadcast receivers and associated equipment - Radio disturbance characteristics
(emissions)
* The Braemac PAC090M power supply (Clipsal Cat. Number 5600P24/3750AU)
is certified to:
Safety standards
IEC 60065 and 60950, EN 60065 and 60950,
K60950, J60950(H14), CNS 13438 ,
CAN/CSA C22.2 No’s. 60950-1 and 60065-03,
UL 60065 and 60950-1 (UL file 161451)
EMC standards
EN 55022, 55024, 61000-3-2 and 61000-3-3
69
Multi Room Audio System
16.0 Warranty
The Multi Room Audio Distribution Unit, Amplifiers and Matrix Switcher carry a two year warranty against manufacturing defects (refer to the
Warranty Statement).
70
Technical Support and Troubleshooting
For further assistance in using this product, consult your nearest
Clipsal Integrated Systems (CIS) Sales Representative or Technical
Support Officer.
Technical Support Contact Numbers
Australia
New Zealand
1300 722 247 (CIS Technical Support Hotline)
0800 888 219 (CIS Technical Support Hotline)
Technical Support email: [email protected]
Sales support email: [email protected]
A list of worldwide contacts, additional product information and technical resources is provided at http://www.clipsal.com/cis/
Product of Clipsal Integrated Systems Pty Ltd
ABN 15 089 444 931
Head Office
12 Park Terrace, Bowden, SA 5007, Australia
Telephone: (+61) 8 8345 9500
Facsimile: (+61) 8 8346 0845
Email: [email protected]
Web: http://www.clipsal.com/cis/ 1031973
advertisement
Related manuals
advertisement