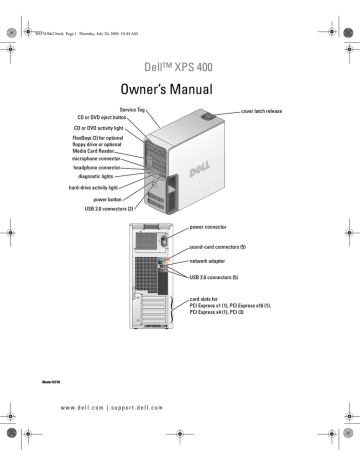
Setting Up and Using Your Computer. Dell Personal Computer XPS 400, XPS 400, XPS 400/Dimension 9150
Add to My manuals148 Pages
advertisement
WD741bk2.book Page 13 Thursday, July 20, 2006 10:44 AM
Setting Up and Using Your Computer
Setting Up a Printer
NOTICE:
Complete the operating system setup before you connect a printer to the computer.
See the documentation that came with the printer for setup information, including how to:
• Obtain and install updated drivers
• Connect the printer to the computer
• Load paper and install the toner or ink cartridge
• Contact the printer manufacturer for technical assistance
Printer Cable
Your printer connects to your computer with a USB cable. Your printer may not come with a printer cable, so if you purchase a cable separately, ensure that it is compatible with your printer. If you purchased a printer cable at the same time you purchased your computer, the cable may arrive in the computer box.
Setting Up and Using Your Computer
13
WD741bk2.book Page 14 Thursday, July 20, 2006 10:44 AM
Connecting a USB Printer
NOTE:
You can connect USB devices while the computer is turned on.
1 Complete the operating system setup, if you have not already done so.
2 Install the printer driver if necessary. See the documentation that came with your printer.
3 Attach the USB printer cable to the USB connectors on the computer and the printer. The
USB connectors fit only one way.
USB connector on computer
USB printer cable
USB connector on printer
Connecting to the Internet
NOTE:
ISPs and ISP offerings vary by country.
To connect to the Internet, you need a modem or network connection and an Internet service provider (ISP), such as AOL or MSN. Your ISP will offer one or more of the following Internet connection options:
• Dial-up connections that provide Internet access through a telephone line. Dial-up connections are considerably slower than DSL and cable modem connections.
• DSL connections that provide high-speed Internet access through your existing telephone line. With a DSL connection, you can access the Internet and use your telephone on the same line simultaneously.
• Cable modem connections that provide high-speed Internet access through your local cable
TV line.
14
Setting Up and Using Your Computer
WD741bk2.book Page 15 Thursday, July 20, 2006 10:44 AM
NOTE:
If you use a dial-up connection, you need an add-in PCI modem expansion card.
If you are using a dial-up connection, connect a telephone line to the modem connector on your computer and to the telephone wall jack before you set up your Internet connection. If you are using a DSL or cable modem connection, contact your ISP for setup instructions.
Setting Up Your Internet Connection
To set up an AOL or MSN connection:
1 Save and close any open files, and exit any open programs.
2 Double-click the MSN Explorer or AOL icon on the Microsoft ®
Windows
®
desktop.
3 Follow the instructions on the screen to complete the setup.
If you do not have an MSN Explorer or AOL icon on your desktop or if you want to set up an
Internet connection with a different ISP:
1 Save and close any open files, and exit any open programs.
2 Click the Start button and click Internet Explorer.
The New Connection Wizard appears.
3 Click Connect to the Internet.
4 In the next window, click the appropriate option:
• If you do not have an ISP and want to select one, click Choose from a list of Internet service providers (ISPs).
• If you have already obtained setup information from your ISP but you did not receive a setup CD, click Set up my connection manually.
• If you have a CD, click Use the CD I got from an ISP.
5 Click Next.
If you selected Set up my connection manually, continue to step 6. Otherwise, follow the
instructions on the screen to complete the setup.
NOTE:
If you do not know which type of connection to select, contact your ISP.
6 Click the appropriate option under How do you want to connect to the Internet?, and then click Next.
7 Use the setup information provided by your ISP to complete the setup.
If you are having problems connecting to the Internet, see "E-Mail, Modem, and Internet
Problems" on page 39. If you cannot connect to the Internet but have successfully connected in the
past, the ISP might have a service outage. Contact your ISP to check the service status, or try connecting again later.
Setting Up and Using Your Computer
15
WD741bk2.book Page 16 Thursday, July 20, 2006 10:44 AM
Playing CDs and DVDs
NOTICE:
Do not press down on the CD or DVD tray when you open or close it. Keep the tray closed when you are not using the drive.
NOTICE:
Do not move the computer when you are playing CDs or DVDs.
1 Press the eject button on the front of the drive.
2 Place the disc, label side up, in the center of the tray.
3 Press the eject button or gently push in the tray.
To format CDs for storing data, to create music CDs, or to copy CDs, see the CD software that came with your computer.
NOTE:
Ensure that you follow all copyright laws when you create CDs.
A CD player includes the following basic buttons:
Play
Move backward within the current track
Pause
Move forward within the current track
Stop
Go to the previous track
16
Setting Up and Using Your Computer
WD741bk2.book Page 17 Thursday, July 20, 2006 10:44 AM
Eject
Go to the next track
A DVD player includes the following basic buttons:
Stop
Restart the current chapter
Play
Fast forward
Pause
Fast reverse
Advance a single frame while in pause mode
Go to the next title or chapter
Continuously play the current title or chapter
Go to the previous title or chapter
Eject
For more information on playing CDs or DVDs, click Help on the CD or DVD player (if available).
Adjusting the Volume
NOTE:
When the speakers are muted, you do not hear the CD or DVD playing.
1 Click the Start button, point to All Programs → Accessories→ Entertainment, and then click
Volume Control.
2 In the Volume Control window, click and drag the bar in the Volume Control column and slide it up or down to increase or decrease the volume.
For more information on volume control options, click Help in the Volume Control window.
Setting Up and Using Your Computer
17
WD741bk2.book Page 18 Thursday, July 20, 2006 10:44 AM
Adjusting the Picture
If an error message notifies you that the current resolution and color depth are using too much memory and preventing DVD playback, adjust the display properties:
1 Click the Start button and click Control Panel.
2 Under Pick a category, click Appearance and Themes.
3 Under Pick a task..., click Change the screen resolution.
4 In the Display Properties window, click and drag the bar in Screen resolution to change the setting to 800 by 600 pixels.
5 Click the drop-down menu under Color quality, and then click Medium (16 bit).
6 Click OK.
Copying CDs and DVDs
NOTE:
Ensure that you observe all copyright laws when creating CDs or DVDs.
This section applies only to computers that have a CD-RW, DVD+/-RW, or CD-RW/DVD
(combo) drive.
NOTE:
The types of CD or DVD drives offered by Dell may vary by country.
The following instructions explain how to make an exact copy of a CD or DVD. You can also use
Sonic DigitalMedia for other purposes, such as creating music CDs from audio files stored on your computer or backing up important data. For help, open Sonic DigitalMedia and then click the question mark icon in the upper-right corner of the window.
How to Copy a CD or DVD
NOTE:
CD-RW/DVD combo drives cannot write to DVD media. If you have a CD-RW/DVD combo drive and you experience recording problems, check for available software patches on the Sonic support website at www.sonic.com.
The DVD-writable drives installed in Dell™ computers can write to and read DVD+/-R,
DVD+/-RW and DVD+R DL (dual layer) media, but cannot write to and may not read
DVD-RAM or DVD-R DL media.
NOTE:
Most commercial DVDs have copyright protection and cannot be copied using Sonic
DigitalMedia.
1 Click the Start button, point to All Programs→ Sonic→ DigitalMedia Projects, and then click Copy.
2 Under the Copy tab, click Disc Copy.
18
Setting Up and Using Your Computer
WD741bk2.book Page 19 Thursday, July 20, 2006 10:44 AM
3 To copy the CD or DVD:
• If you have one CD or DVD drive, ensure that the settings are correct and click the Disc
Copy button. The computer reads your source CD or DVD and copies the data to a temporary folder on your computer hard drive.
When prompted, insert a blank CD or DVD into the drive and click OK.
• If you have two CD or DVD drives, select the drive into which you have inserted your source CD or DVD and click the Disc Copy button. The computer copies the data from the source CD or DVD to the blank CD or DVD.
Once you have finished copying the source CD or DVD, the CD or DVD that you have created automatically ejects.
Using Blank CDs and DVDs
CD-RW drives can write to CD recording media only (including high-speed CD-RW) while
DVD-writable drives can write to both CD and DVD recording media.
Use blank CD-Rs to record music or permanently store data files. After creating a CD-R, you cannot write to that CD-R again (see the Sonic documentation for more information). Use blank CD-RWs to write to CDs or to erase, rewrite, or update data on CDs.
Blank DVD+/-Rs can be used to permanently store large amounts of information. After you create a DVD+/-R disc, you may not be able to write to that disc again if the disc is "finalized" or
"closed" during the final stage of the disc creation process. Use blank DVD+/-RWs if you plan to erase, rewrite, or update information on that disc later.
CD-Writable Drives
Media Type
CD-R
CD-RW
DVD-Writable Drives
Read
Yes
Yes
Write
Yes
Yes
Rewritable
No
Yes
Media Type
CD-R
CD-RW
DVD+R
DVD-R
DVD+RW
DVD-RW
DVD+R DL
Read
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Write
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Rewritable
Yes
Yes
No
No
Yes
No
No
Setting Up and Using Your Computer
19
WD741bk2.book Page 20 Thursday, July 20, 2006 10:44 AM
Media Type
DVD-R DL
DVD-RAM
Read
Maybe
Maybe
Write
No
No
Rewritable
No
No
Helpful Tips
• Use Microsoft
®
Windows
®
Explorer to drag and drop files to a CD-R or CD-RW only after you start Sonic DigitalMedia and open a DigitalMedia project.
• Use CD-Rs to burn music CDs that you want to play in regular stereos. CD-RWs do not play in most home or car stereos.
• You cannot create audio DVDs with Sonic DigitalMedia.
• Music MP3 files can be played only on MP3 players or on computers that have MP3 software installed.
• Commercially available DVD players used in home theater systems may not support all available DVD formats. For a list of formats supported by your DVD player, see the documentation provided with your DVD player or contact the manufacturer.
• Do not burn a blank CD-R or CD-RW to its maximum capacity; for example, do not copy a
650-MB file to a blank 650-MB CD. The CD-RW drive needs 1–2 MB of the blank space to finalize the recording.
• Use a blank CD-RW to practice CD recording until you are familiar with CD recording techniques. If you make a mistake, you can erase the data on the CD-RW and try again. You can also use blank CD-RWs to test music file projects before you record the project permanently to a blank CD-R.
• See the Sonic website at www.sonic.com for additional information.
Using a Media Card Reader (Optional)
Use the Media Card Reader to transfer data directly to your computer.
The Media Card Reader supports the following memory types:
• xD-Picture Card
• SmartMedia (SMC)
• CompactFlash Type I and II (CF I/II)
• MicroDrive Card
• SecureDigital Card (SD)
• MultiMediaCard (MMC)
• Memory Stick (MS/MS Pro)
20
Setting Up and Using Your Computer
WD741bk2.book Page 21 Thursday, July 20, 2006 10:44 AM
For information on installing a Media Card Reader, see "Installing a Media Card Reader" on page 101.
xD-Picture Card and SmartMedia (SMC)
Memory Stick
(MS/MS Pro)
CompactFlash Type I and II (CF I/II) and
MicroDrive Card
SecureDigital Card (SD)/
MultiMediaCard (MMC)
To use the Media Card Reader:
1 Check the media or card to determine the proper orientation for insertion.
2 Slide the media or card into the appropriate slot until it is completely seated in the connector.
If you encounter resistance, do not force the media or card. Check the card orientation and try again.
Connecting Two Monitors
CAUTION:
Before you begin any of the procedures in this section, follow the safety instructions in the
Product Information Guide.
NOTE:
If you are connecting two monitors that have VGA connectors, you must have the optional DVI adapter. If you are connecting two flat-panel monitors, at least one of them must have a VGA connector. If you are connecting a television, you may connect only one monitor (VGA or DVI) in addition to the television.
Setting Up and Using Your Computer
21
WD741bk2.book Page 22 Thursday, July 20, 2006 10:44 AM
If you purchased a graphics card that supports dual monitors, follow these instructions to connect and enable your monitors. The instructions tell you how to connect either two monitors (each with a VGA connector), one monitor with a VGA connector and one monitor with a DVI connector, or a TV.
Connecting Two Monitors With VGA Connectors
1 Follow the procedures in "Before You Begin" on page 63.
2 Connect one of the monitors to the VGA (blue) connector on the back of the computer.
3 Connect the other monitor to the optional DVI adapter and connect the DVI adapter to the
DVI (white) connector on the back of the computer.
optional DVI adapter
DVI (white) connector
TV-OUT connector
VGA (blue) connector
Connecting One Monitor With a VGA Connector and One Monitor With a DVI Connector
1 Follow the procedures in "Before You Begin" on page 63.
2 Connect the VGA connector on the monitor to the VGA (blue) connector on the back of the computer.
3 Connect the DVI connector on the other monitor to the DVI (white) connector on the back of the computer.
22
Setting Up and Using Your Computer
WD741bk2.book Page 23 Thursday, July 20, 2006 10:44 AM
Connecting a TV
NOTE:
To connect a TV to your computer, you must purchase an S-video cable, which is available at most consumer electronics stores. An S-video cable is not included with your computer.
1 Follow the procedures in "Before You Begin" on page 63.
2 Connect one end of the S-video cable to the TV-OUT connector on the back of the computer.
3 Connect the other end of the S-video cable to the S-video input connector on your TV.
4 Connect the VGA or DVI monitor.
Changing the Display Settings
1 After you connect the monitor(s) or TV, turn on the computer.
The Microsoft
®
Windows
®
desktop displays on the primary monitor.
2 Enable clone mode or extended desktop mode in the display settings.
• In clone mode, both monitors display the same image.
• In extended desktop mode, you can drag objects from one screen to the other, effectively doubling the amount of viewable work space.
For information on changing the display settings for your graphics card, see the user’s guide in the
Help and Support Center (click the Start button, click Help and Support, click User and system guides, click Device guides, and then click the guide for your graphics card).
Setting Up a Home and Office Network
Connecting to a Network Adapter
NOTICE:
Plug the network cable into the network adapter connector on the computer. Do not plug the network cable into the modem connector on the computer. Do not plug a network cable into a telephone wall jack.
1 Connect the network cable to the network adapter connector on the back of your computer.
Insert the cable until it clicks into place, and then gently pull it to ensure that it is secure.
2 Connect the other end of the network cable to a network device.
Setting Up and Using Your Computer
23
WD741bk2.book Page 24 Thursday, July 20, 2006 10:44 AM network adapter connector network device network adapter connector on computer network cable
Network Setup Wizard
The Microsoft
®
Windows
®
XP operating system provides a Network Setup Wizard to guide you through the process of sharing files, printers, or an Internet connection between computers in a home or small office.
1 Click the Start button, point to All Programs→ Accessories→ Communications, and then click Network Setup Wizard.
2 On the welcome screen, click Next.
3 Click Checklist for creating a network.
NOTE:
Selecting the connection method This computer connects directly to the Internet enables the integrated firewall provided with Windows XP Service Pack.
4 Complete the checklist and required preparations.
5 Return to the Network Setup Wizard and follow the instructions on the screen.
Power Management
The Microsoft
®
Windows
®
XP power management features can reduce the amount of electricity your computer uses when it is on and you are not using it. You can reduce power to just the monitor or the hard drive, or you can use standby mode or hibernate mode to reduce power to the entire computer. When the computer exits from a power conservation mode, the Windows desktop is restored to the state it was in before it entered the mode.
NOTE:
Windows XP Professional includes security and networking features not available in
Windows XP Home Edition. When a Windows XP Professional computer is connected to a network, different options related to security and networking appear in certain windows.
24
Setting Up and Using Your Computer
WD741bk2.book Page 25 Thursday, July 20, 2006 10:44 AM
Standby Mode
Standby mode conserves power by turning off the display and the hard drive after a time-out.
When the computer exits from standby mode, it returns to the operating state it was in before it entered standby mode.
To set standby mode to automatically activate after a defined period of inactivity:
1 Click the Start button and click Control Panel.
2 Under Pick a category, click Performance and Maintenance.
3 Under or pick a Control Panel icon, click Power Options.
To immediately activate standby mode without a period of inactivity, click the Start button, click
Turn Off Computer, and then click Stand by.
To exit from standby mode, press a key on the keyboard or move the mouse.
NOTICE:
If your computer loses power while in standby mode, it may lose data.
Hibernate Mode
Hibernate mode conserves power by copying system data to a reserved area on the hard drive and then completely turning off the computer. When the computer exits from hibernate mode, the desktop is restored to the state it was in before it entered hibernate mode.
To activate hibernate mode:
1 Click the Start button and click Control Panel.
2 Under Pick a category, click Performance and Maintenance.
3 Under or pick a Control Panel icon, click Power Options.
4 Define your hibernate settings on the Power Schemes tab, Advanced tab, and Hibernate tab.
To exit from hibernate mode, press the power button. The computer may take a short time to exit from hibernate mode. Pressing a key on the keyboard or moving the mouse does not bring the computer out of hibernation, because the keyboard and the mouse do not function when the computer is in hibernate mode.
Because hibernate mode requires a special file on your hard drive with enough disk space to store the contents of the computer memory, Dell creates an appropriately sized hibernate mode file before shipping the computer to you. If the computer’s hard drive becomes corrupted,
Windows XP recreates the hibernate file automatically.
Power Options Properties
Define your standby mode settings, hibernate mode settings, and other power settings in the Power
Options Properties window.
To access the Power Options Properties window:
1 Click the Start button and click Control Panel.
2 Under Pick a category, click Performance and Maintenance.
Setting Up and Using Your Computer
25
WD741bk2.book Page 26 Thursday, July 20, 2006 10:44 AM
3 Under or pick a Control Panel icon, click Power Options.
4 Define your power settings on the Power Schemes tab, Advanced tab, and Hibernate tab.
Power Schemes Tab
Each standard power setting is called a scheme. If you want to select one of the standard Windows schemes installed on your computer, choose a scheme from the Power schemes drop-down menu.
The settings for each scheme appear in the fields below the scheme name. Each scheme has different settings for starting standby mode or hibernate mode, turning off the monitor, and turning off the hard drive.
The Power schemes drop-down menu displays the following schemes:
• Always On (default) — If you want to use your computer with no power conservation.
• Home/Office Desk — If you use your computer as a home or office computer and you require minimal power conservation.
• Presentation — If you want your computer to run without interruption (using no power conservation).
• Minimal Power Management — If you want your computer to run with minimal power conservation.
• Max Battery — If your computer is a portable computer and you run your computer from batteries for extended periods of time.
If you want to change the default settings for a scheme, click the drop-down menu in the Turn off monitor, Turn off hard disks, System stand by, or System hibernates field, and then select a timeout from the displayed list. Changing the time-out for a scheme field permanently changes the default settings for that scheme, unless you click Save As and enter a new name for the changed scheme.
NOTICE:
If you set the hard drive (hard disk) to time-out before the monitor does, your computer may appear to be locked up. To recover, press any key on the keyboard or click the mouse. To avoid this problem, always set the monitor to time-out before the hard drive.
Advanced Tab
The Advanced tab allows you to:
• Place the power options icon in the Windows taskbar for quick access.
• Set the computer to prompt you for your Windows password before the computer exits from standby mode or hibernate mode.
• Program the power button to activate standby mode, activate hibernate mode, or turn off the computer.
To program these functions, click an option from the corresponding drop-down menu and click OK.
26
Setting Up and Using Your Computer
WD741bk2.book Page 27 Thursday, July 20, 2006 10:44 AM
Hibernate Tab
The Hibernate tab allows you to enable hibernate mode. If you want to use the hibernate settings you defined on the Power Schemes tab, click the Enable hibernate support check box on the
Hibernate tab.
For more information on power management options:
1 Click the Start button and click Help and Support.
2 In the Help and Support window, click Performance and maintenance.
3 In the Performance and maintenance window, click Conserving power on your computer.
IEEE 1394
IEEE 1394 is a digital interface that can move large amounts of data between computers and peripheral devices. IEEE 1394 is ideal for use with multimedia devices because it speeds the transfer of data and large files, which enables a computer to connect directly to devices such as digital video cameras.
NOTE:
The connector can accept 4-pin IEEE 1394 devices with the use of an adapter.
Your computer may have an optional front IEEE 1394 connector (see "Front View of the
Computer" on page 65). This connector is only available if you purchased an add-in card that uses
IEEE 1394. To purchase a card, contact Dell.
Hyper-Threading
Hyper-Threading is an Intel
®
technology that can enhance overall computer performance by allowing one physical processor to function as two logical processors, capable of performing certain tasks simultaneously. It is recommended that you use the Microsoft
®
Windows
®
XP Service Pack 1
(SP1) or later operating system because Windows XP is optimized to take advantage of
Hyper-Threading technology. While many programs can benefit from Hyper-Threading, some programs have not been optimized for Hyper-Threading and may require an update from the software manufacturer. Contact the software manufacturer for updates and information about using Hyper-Threading with your software.
To determine if your computer is using Hyper-Threading technology:
1 Click the Start button, right-click My Computer, and then click Properties.
2 Click Hardware and click Device Manager.
3 In the Device Manager window, click the plus (+) sign next to Processors. If Hyper-Threading is enabled, the processor is listed twice.
You can enable or disable Hyper-Threading through system setup. For more information on
accessing system setup, see page 114. For more information on Hyper-Threading, search the
Knowledge Base on the Dell Support website at support.dell.com.
Setting Up and Using Your Computer
27
WD741bk2.book Page 28 Thursday, July 20, 2006 10:44 AM
About Your RAID Configuration
This section provides an overview of the RAID configuration that you might have selected when you purchased your computer. Although several RAID configurations are available, Dell offers either a RAID level 0 configuration or a RAID level 1 configuration for its Dimension™ computers. A RAID level 0 configuration is recommended for high-performance gaming, and a
RAID level 1 configuration is recommended for the data integrity requirements of digital photography and audio.
The Intel
®
RAID controller on your computer can only create a RAID level 0 configuration using two or three physical drives. If a third drive is present, then that drive can be made part of a RAID level 0 configuration using the Intel RAID configuration program, or it can be used as a
spare drive in a RAID level 1 configuration (see "Creating a Spare Hard Drive" on page 35). The
drives should be the same size in order to ensure that the larger drive does not contain unallocated (and therefore unusable) space.
NOTE:
RAID levels do not represent a hierarchy. A RAID level 1 configuration is not inherently better or worse than a RAID level 0 configuration.
RAID Level 0 Configuration
A RAID level 0 configuration uses a storage technique known as "data striping" to provide a high data access rate. Data striping is a method of writing consecutive segments, or stripes, of data sequentially across the physical drives to create a large virtual drive. Data striping allows one of the drives to read data while the other drive is searching for and reading the next block.
serial ATA RAID configured for
RAID level 0 segment 1 segment 3 segment 5 hard drive 1 segment 2 segment 4 segment 6 hard drive 2
Another advantage of a RAID level 0 configuration is that it utilizes the full capacities of the drives. For example, if you have two 120-GB drives installed, you have 240 GB on which to store data.
28
Setting Up and Using Your Computer
WD741bk2.book Page 29 Thursday, July 20, 2006 10:44 AM
NOTICE:
Because RAID level 0 configurations provide no data redundancy, if one drive fails, then the data on the other drive is also inaccessible. Therefore, ensure that you perform regular backups when you use a RAID level 0 configuration.
RAID Level 1 Configuration
RAID level 1 uses a data-redundancy storage technique known as "mirroring." When data is written to the primary drive, it is then duplicated, or mirrored, on the other drive. A RAID level 1 configuration sacrifices high data-access rates for its data redundancy advantages.
serial ATA RAID configured for
RAID level 1 segment 1 segment 2 segment 3 segment 4 segment 5 segment 6 hard drive 1 segment 1 duplicated segment 2 duplicated segment 3 duplicated segment 4 duplicated segment 5 duplicated segment 6 duplicated hard drive 2
If a drive failure occurs, subsequent read and write operations are directed to the surviving drive.
A replacement drive can then be rebuilt using the data from the surviving drive. Also, because data is duplicated on both drives, a RAID level 1 configuration using two 120-GB hard drives collectively has a maximum of 120 GB on which to store data.
Configuring Your Computer for RAID
At some point you may want to configure your computer for RAID if you did not select a RAID configuration when you purchased your computer. You must have at least two hard drives installed in your computer to set up a RAID configuration. For instructions on how to install a
You can use one of two methods to configure RAID hard drive volumes. One method uses the
Intel
®
RAID Option ROM utility and is performed before you install the operating system onto the hard drive. The second method uses the Intel Matrix Storage Manager, or Intel Matrix
Storage Console, and this method is performed after you have installed the operating system
Setting Up and Using Your Computer
29
WD741bk2.book Page 30 Thursday, July 20, 2006 10:44 AM and the Intel Matrix Storage Console. Both methods require that you set your computer to
RAID-enabled mode before starting any of the RAID configuration procedures in this document.
Setting Your Computer to RAID-Enabled Mode
1 Enter system setup (see page 113).
2 Press the up- and down-arrow keys to highlight Drives, and press <Enter>.
3 Press the up- and down-arrow keys to highlight SATA Operation, and press <Enter>.
4 Press the left- and right-arrow keys to highlight RAID On, press <Enter>, and then press <Esc>.
NOTE:
For more information about RAID options, see "System Setup Options" on page 116.
5 Press the left- and right-arrow keys to highlight Save/Exit, and press <Enter> to exit system setup and resume the boot process.
Configuring for RAID Using the Intel
®
RAID Option ROM Utility
NOTE:
Although any size drives may be used to create a RAID configuration using the Intel RAID Option
ROM utility, ideally the drives should be of equal size. In a RAID level 0 configuration, the size of the configuration will be the size of the smallest drive multiplied by the number (two) of drives in the configuration. In a RAID level 1 configuration, the size of the configuration will be the smaller of the two drives used.
Creating a RAID Level 0 Configuration
NOTICE:
You will lose any data on your hard drives when you create a RAID configuration using the following procedure. Back up data you want to keep before continuing.
NOTE:
Use the following procedure only if you are reinstalling your operating system. Do not use the following procedure to migrate an existing storage configuration to RAID level 0 configuration.
1 Set your computer to RAID-enabled mode (see page 30).
2 Press <Ctrl><i> when you are prompted to enter the Intel ®
RAID Option ROM utility.
3 Press the up- and down-arrow keys to highlight Create RAID Volume, and press <Enter>.
4 Enter a RAID volume name or accept the default, and press <Enter>.
5 Press the up- and down-arrow keys to select RAID0(Stripe), and press <Enter>.
6 If there are more than two hard drives available, press the up- and down-arrow keys and spacebar to select the two or three drives you want to use to make up your configuration, and then press <Enter>.
NOTE:
Select the strip size closest to the size of the average file you want to store on the RAID volume. If you do not know the average file size, choose 128 KB as your strip size.
7 Press the up- and down-arrow keys to change the strip size, and press <Enter>.
30
Setting Up and Using Your Computer
WD741bk2.book Page 31 Thursday, July 20, 2006 10:44 AM
8 Select the desired capacity for the volume, and press <Enter>. The default value is the maximum available size.
9 Press <Enter> to create the volume.
10 Press <y> to confirm that you want to create the RAID volume.
11 Confirm that the correct volume configuration is displayed on the main Intel
®
RAID Option
ROM utility screen.
12 Press the up- and down-arrow keys to select Exit, and press <Enter>.
13 Install the operating system (see "Using Microsoft Windows XP System Restore" on page 60).
Creating a RAID Level 1 Configuration
1 Set your computer to RAID-enabled mode (see page 30).
2 Press <Ctrl><i> when you are prompted to enter the Intel RAID Option ROM utility.
3 Use the up- and down-arrow keys to highlight Create RAID Volume, and press <Enter>.
4 Enter a RAID volume name or accept the default, and press <Enter>.
5 Use the up- and down-arrow keys to select RAID1(Mirror), and press <Enter>.
6 If there are more than two hard drives available, press the up- and down-arrow keys and spacebar to select the two drives you want to use to make up your volume, and then press
<Enter>.
7 Select the desired capacity for the volume, and press <Enter>. The default value is the maximum available size.
8 Press <Enter> to create the volume.
9 Press <y> to confirm that you want to create the RAID volume.
10 Confirm that the correct volume configuration is displayed on the main Intel RAID Option
ROM utility screen.
11 Use the up- and down-arrow keys to select Exit, and press <Enter>.
12 Install the operating system (see "Using Microsoft Windows XP System Restore" on page 60).
Deleting a RAID Volume
NOTE:
When you perform this operation, all data on the RAID drives will be lost.
NOTE:
If your computer currently boots to RAID and you delete the RAID volume in the Intel RAID Option
ROM utility, your computer will become unbootable.
1 Press <Ctrl><i> when you are prompted to enter the Intel RAID Option ROM utility.
2 Use the up- and down-arrow keys to highlight Delete RAID Volume, and press <Enter>.
3 Use the up- and down-arrow keys to highlight the RAID volume you want to delete, and press
<Delete>.
Setting Up and Using Your Computer
31
WD741bk2.book Page 32 Thursday, July 20, 2006 10:44 AM
4 Press <y> to confirm the deletion of the RAID volume.
5 Press <Esc> to exit the Intel RAID Option ROM utility.
Configuring for RAID Using the Intel
®
Application Accelerator
If you already have one hard drive with the operating system installed on it, and you want to add a second hard drive and reconfigure both drives into a RAID volume without losing the existing
operating system and any data, you need to use the migrating option (see "Migrating to a RAID
Level 0 Configuration" on page 33 or "Migrating to a RAID Level 1 Configuration" on page 34).
Create a RAID level 0 volume or RAID level 1 volume only when:
• You are adding two new drives to an existing single-drive computer (and the operating system is on the single drive), and you want to configure the two new drives into a RAID volume.
• You already have a two-hard drive computer configured into a volume, but you still have some space left on the volume that you want to designate as a second RAID volume.
Creating a RAID Level 0 Configuration
NOTE:
When you perform this operation, all data on the RAID drives will be lost.
1 Set your computer to RAID-enabled mode (see page 30).
2 Click Start and point to Programs→ Intel(R) Application Accelerator → Intel Matrix
Storage Manager to launch the Intel
®
Storage Utility.
NOTE:
If you do not see an Actions menu option, you have not yet set your computer to RAID-enabled
3 On the Actions menu, select Create RAID Volume to launch the Create RAID Volume
Wizard, and then click Next.
4 On the Select Volume Location screen, click the first hard drive you want to include in your
RAID level 0 volume, and then click the right arrow.
5 Click a second hard drive. To add a third hard drive in your RAID level 0 volume, click the right arrow and click on the third drive until three drives appear in the Selected window, and then click Next.
6 In the Specify Volume Size window, click the Volume Size desired, and then click Next.
7 Click Finish to create the volume, or click Back to make changes.
Creating a RAID Level 1 Configuration
NOTE:
When you perform this operation, all data on the RAID drives will be lost.
1 Set your computer to RAID-enabled mode (see page 30).
2 Click the Start button and point to Programs→ Intel(R) Application Accelerator→ Intel
Matrix Storage Manager to launch the Intel
®
Storage Utility.
32
Setting Up and Using Your Computer
WD741bk2.book Page 33 Thursday, July 20, 2006 10:44 AM
NOTE:
If you do not see an Actions menu option, you have not yet set your computer to RAID-enabled
3 On the Actions menu, select Create RAID Volume to launch the Create RAID Volume
Wizard.
4 Click Next at the first screen.
5 Confirm the volume name, select RAID 1 as the RAID level, and then click Next to continue.
6 On the Select Volume Location screen, click the first hard drive you want to use to create your RAID level 0 volume, and then click the right arrow. Click a second hard drive until two drives appear in the Selected window, and then click Next.
7 In the Specify Volume Size window, select the Volume Size desired and click Next.
8 Click Finish to create the volume, or click Back to make changes.
9 Follow Microsoft Windows procedures for creating a partition on the new RAID volume.
Deleting a RAID Volume
NOTE:
While this procedure deletes the RAID 1 volume, it also splits the RAID 1 volume into two non-
RAID hard drives with a partition, and leaves any existing data files intact. Deleting a RAID 0 volume, however, destroys all data on the volume.
Matrix Storage Manager to launch the Intel
®
Storage Utility.
2 Right-click the Volume icon of the RAID volume you want to delete, and select Delete Volume.
3 On the Delete RAID Volume Wizard screen, click Next.
4 Highlight the RAID volume you want to delete in the Available box, click the right-arrow button to move the highlighted RAID volume into the Selected box, and then click Next.
5 Click Finish to delete the volume.
Migrating to a RAID Level 0 Configuration
1 Set your computer to RAID-enabled mode (see page 30).
2 Click the Start button and point to All Programs→ Intel(R) Application Accelerator→ Intel
Matrix Storage Manager to launch the Intel
®
Storage Utility.
NOTE:
If you do not see an Actions menu option, you have not yet set your computer to RAID-enabled
3 On the Actions menu, select Create RAID Volume From Existing Hard Drive to launch the
Migration Wizard.
4 Click Next on the Migration Wizard screen.
5 Enter a RAID volume name or accept the default.
Setting Up and Using Your Computer
33
WD741bk2.book Page 34 Thursday, July 20, 2006 10:44 AM
34
6 From the drop-down box, select RAID 0 as the RAID level.
NOTE:
Select the strip size closest to the size of the average file you want to store on the RAID volume. If you do not know the average file size, choose 128 KB as your strip size.
7 Select the appropriate strip size from the drop-down box, and then click Next.
NOTE:
Select the hard drive that you want to use as your source hard drive (it should be the hard drive containing the data or operating system files that you want to keep on the RAID volume).
8 On the Select Source Hard Drive screen, double-click the hard drive from which you want to migrate, and click Next.
9 On the Select Member Hard Drive screen, double-click the hard drive(s) to select the member drive(s) to span the stripe array, and click Next.
10 On the Specify Volume Size screen, select the Volume Size you want, and click Next.
NOTE:
In the following step, you will lose all data contained on the member drive.
11 Click Finish to start migrating, or click Back to make changes. You can use your computer normally during the migration process.
Migrating to a RAID Level 1 Configuration
1 Set your computer to RAID-enabled mode (see page 30).
Matrix Storage Manager to launch the Intel
®
Storage Utility.
NOTE:
If you do not see an Actions menu option, you have not yet set your computer to RAID-enabled
3 On the Actions menu, click Create RAID Volume From Existing Hard Drive to launch the
Migration Wizard.
4 Click Next on the first Migration Wizard screen.
5 Enter a RAID volume name or accept the default.
6 From the drop-down box, select RAID 1 as the RAID level.
NOTE:
Select the hard drive that you want to use as your source hard drive (it should be the hard drive containing the data or operating system files that you want to keep on the RAID volume).
7 On the Select Source Hard Drive screen, double-click the hard drive from which you want to migrate, and click Next.
8 On the Select Member Hard Drive screen, double-click the hard drive to select the member drive that you want to act as the mirror in the configuration, and click Next.
9 On the Specify Volume Size screen, select the volume size you want, and click Next.
NOTE:
In the following step, you will lose all data contained on the member drive.
10 Click Finish to start migrating, or click Back to make changes. You can use your computer normally during migration process.
Setting Up and Using Your Computer
WD741bk2.book Page 35 Thursday, July 20, 2006 10:44 AM
Creating a Spare Hard Drive
A spare hard drive may be created with a RAID level 1 configuration. The spare hard drive will not be recognized by the operating system, but you will be able to see the spare drive from within Disk Manager or the Intel RAID Option ROM utility. When a member of the RAID level 1 configuration is broken, the computer automatically rebuilds the mirror configuration using the spare hard drive as the broken member’s replacement.
To Mark a Drive as a Spare Hard Drive:
1 Click the Start button and point to Programs→ Intel(R) Application Accelerator→ Intel
Matrix Storage Manager to launch the Intel
®
Storage Utility.
2 Right-click the hard drive you want to mark as a spare hard drive.
3 Click Mark as Spare.
To Remove Spare Marking From a Spare Hard Drive:
1 Right-click the spare hard drive icon.
2 Click Reset Hard Drive to Non-RAID
Rebuilding a Degraded RAID Level 1 Configuration
If your computer does not have a spare hard drive, and the computer has reported a degraded
RAID level 1 volume, you can manually rebuild the computer’s redundancy mirror to a new hard drive by performing the following steps:
1 Click the Start button and point to Programs→ Intel(R) Application Accelerator→ Intel
Matrix Storage Manager to launch the Intel
®
Storage Utility.
2 Right-click the available hard drive to which you want to rebuild the RAID level 1 volume, and click Rebuild to this Disk.
You can use your computer while the computer is rebuilding the RAID level 1 volume.
Understanding Intel
®
Viiv™ Technology (Optional)
Intel Viiv technology is a technology aimed at the digital home enthusiast that includes:
• A BIOS with Quick Resume
• Device drivers
This technology allows the user’s system to quickly return to an active state after non-use
Intel Viiv technology is an option for systems that are ordered with Microsoft
®
Windows
®
XP
Media Center Edition 2005 and dual core processors.
Setting Up and Using Your Computer
35
WD741bk2.book Page 36 Thursday, July 20, 2006 10:44 AM
Using Intel
®
Viiv™ Quick Resume Technology (Optional)
When running in the Intel Viiv Quick Resume Technology (QRT) mode, your power button is used as a quick on/off feature. Pressing the power button once causes the display to go blank and the audio to mute. In this mode, the computer is still operating as indicated by the power button indicator and diagnostic lights 1, 2, and 4 being lit. Also, you may notice that the hard drive indicator may blink when the hard drive is being accessed by an external device.
To resume normal computer operation, briefly press the power button, press any key on the keyboard, move the mouse, or press a button on the optional Microsoft
®
Windows
®
XP Media
Center Edition 2005 remote control.
Enabling the QRT Feature in System Setup
The QRT drivers must be installed before this feature becomes active. These drivers are installed when this option is ordered. Also, Quick Resume is enabled in system setup when this feature is ordered.
1 Enter system setup (see page 114).
2 Press the arrow keys to highlight the Power Management menu option and press <Enter> to access the menu.
3 Press the up- and down-arrow keys to highlight the Quick Resume option and press <Enter> to access the menu.
4 Press the left- and right-arrow keys to highlight the On option and press <Enter> to enable the Quick Resume feature.
Enabling the QRT feature in the Operating system
1 Click the Start button and click Control Panel.
2 Under Pick a category, click Performance and Maintenance.
3 Under or pick a Control Panel icon, click Power Options.
4 Click the Away tab.
5 Ensure that the check boxes for Enable away mode and Options are checked.
6 Click the Advanced tab.
7 From the When I press the power button on my computer drop-down menu, select Do
Nothing.
8 From the When I press the sleep button on my computer drop-down menu, select Do
Nothing.
36
Setting Up and Using Your Computer
advertisement
Related manuals
advertisement
Table of contents
- 1 Owner’s Manual
- 3 Contents
- 9 Finding Information
- 13 Setting Up and Using Your Computer
- 13 Setting Up a Printer
- 13 Printer Cable
- 14 Connecting a USB Printer
- 14 Connecting to the Internet
- 15 Setting Up Your Internet Connection
- 16 Playing CDs and DVDs
- 17 Adjusting the Volume
- 18 Adjusting the Picture
- 18 Copying CDs and DVDs
- 18 How to Copy a CD or DVD
- 19 Using Blank CDs and DVDs
- 20 Helpful Tips
- 20 Using a Media Card Reader (Optional)
- 21 Connecting Two Monitors
- 22 Connecting Two Monitors With VGA Connectors
- 22 Connecting One Monitor With a VGA Connector and One Monitor With a DVI Connector
- 23 Connecting a TV
- 23 Changing the Display Settings
- 23 Setting Up a Home and Office Network
- 23 Connecting to a Network Adapter
- 24 Network Setup Wizard
- 24 Power Management
- 25 Standby Mode
- 25 Hibernate Mode
- 25 Power Options Properties
- 27 IEEE 1394
- 27 Hyper-Threading
- 28 About Your RAID Configuration
- 28 RAID Level 0 Configuration
- 29 RAID Level 1 Configuration
- 29 Configuring Your Computer for RAID
- 30 Configuring for RAID Using the Intel® RAID Option ROM Utility
- 32 Configuring for RAID Using the Intel® Application Accelerator
- 35 Understanding Intel® Viiv™ Technology (Optional)
- 36 Using Intel® Viiv™ Quick Resume Technology (Optional)
- 36 Enabling the QRT Feature in System Setup
- 36 Enabling the QRT feature in the Operating system
- 37 Solving Problems
- 37 Troubleshooting Tips
- 37 Battery Problems
- 38 Drive Problems
- 38 CD and DVD drive problems
- 39 Hard drive problems
- 39 E-Mail, Modem, and Internet Problems
- 41 Error Messages
- 42 Media Card Reader Problems
- 42 Keyboard Problems
- 43 Lockups and Software Problems
- 43 The computer does not start up
- 43 The computer stops responding
- 43 A program stops responding
- 43 A program crashes repeatedly
- 44 A program is designed for an earlier Windows operating system
- 44 A solid blue screen appears
- 44 Other software problems
- 45 Memory Problems
- 45 Mouse Problems
- 46 Network Problems
- 47 Power Problems
- 48 Printer Problems
- 48 Scanner Problems
- 49 Sound and Speaker Problems
- 49 No sound from speakers
- 50 No sound from headphones
- 50 Video and Monitor Problems
- 50 If the screen is blank
- 51 If the screen is difficult to read
- 53 Troubleshooting Tools
- 53 Diagnostic Lights
- 56 Dell Diagnostics
- 56 Dell Diagnostics Main Menu
- 57 Drivers
- 57 What Is a Driver?
- 58 Identifying Drivers
- 58 Reinstalling Drivers
- 59 Resolving Software and Hardware Incompatibilities
- 59 Restoring Your Operating System
- 60 Using Microsoft Windows XP System Restore
- 61 Using Dell PC Restore by Symantec
- 63 Removing and Installing Parts
- 63 Before You Begin
- 63 Recommended Tools
- 63 Turn Off Your Computer
- 64 Before Working Inside Your Computer
- 65 Front View of the Computer
- 67 Back View of the Computer
- 68 Removing the Computer Cover
- 70 Inside View of Your Computer
- 71 System Board Components
- 72 Memory
- 72 Memory Overview
- 74 Installing Memory
- 76 Removing Memory
- 76 Cards
- 77 PCI Cards
- 81 PCI Express Cards
- 89 Drive Panels
- 89 Removing the Drive Panel
- 90 Removing the Drive-Panel Insert
- 90 Replacing the Drive-Panel Insert
- 91 Replacing the Drive Panel
- 92 Drives
- 92 General Installation Guidelines
- 92 Hard Drive
- 93 Removing a Hard Drive
- 94 Installing a Hard Drive
- 95 Adding a Second Hard Drive
- 96 Floppy Drive
- 96 Removing a Floppy Drive
- 98 Installing a Floppy Drive
- 99 Media Card Reader
- 99 Removing a Media Card Reader
- 101 Installing a Media Card Reader
- 102 CD/DVD Drive
- 103 Removing a CD/DVD Drive
- 104 Installing a CD/DVD Drive
- 106 Battery
- 106 Replacing the Battery
- 107 Replacing the Computer Cover
- 109 Appendix
- 109 Specifications
- 113 System Setup
- 113 Overview
- 114 Entering System Setup
- 116 System Setup Options
- 119 Boot Sequence
- 121 Clearing Forgotten Passwords
- 122 Clearing CMOS Settings
- 122 Cleaning Your Computer
- 122 Computer, Keyboard, and Monitor
- 123 Mouse
- 123 Floppy Drive
- 123 CDs and DVDs
- 123 Dell Technical Support Policy (U.S. Only)
- 124 Definition of "Dell-Installed" Software and Peripherals
- 124 Definition of "Third-Party" Software and Peripherals
- 124 FCC Notices (U.S. Only)
- 125 Class A
- 125 Class B
- 126 FCC Identification Information
- 126 Contacting Dell
- 145 Index