OTHER RECORDING FUNCTIONS . Casio QV-R3, QV-R3 Part 2, QV-R4 Part 2, QV-R4
Add to my manuals
51 Pages
advertisement
OTHER RECORDING FUNCTIONS
OTHER RECORDING FUNCTIONS
This chapter describes the other powerful features and functions that are available for recording.
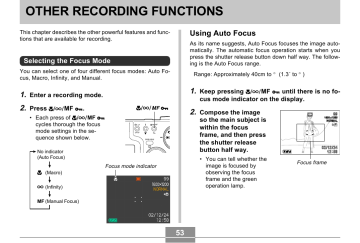
Selecting the Focus Mode
You can select one of four different focus modes: Auto Focus, Macro, Infinity, and Manual.
Using Auto Focus
As its name suggests, Auto Focus focuses the image automatically. The automatic focus operation starts when you press the shutter release button down half way. The following is the Auto Focus range.
Range: Approximately 40cm to
∞
(1.3´ to
∞
)
1.
Enter a recording mode.
2.
Press MF .
• Each press of MF cycles thorough the focus mode settings in the sequence shown below.
No indicator
(Auto Focus)
(Macro)
(Infinity)
MF (Manual Focus)
DPOF
MF
PREVIEW
Focus mode indicator
MF
1.
Keep pressing MF until there is no focus mode indicator on the display.
2.
Compose the image so the main subject is within the focus frame, and then press the shutter release button half way.
• You can tell whether the image is focused by observing the focus frame and the green operation lamp.
Focus frame
IN
53
OTHER RECORDING FUNCTIONS
When you see this:
Green focus frame
Green operation lamp
Green flashing focus frame
Flashing green operation lamp
It means this:
The image is focused.
The image is not in focus.
3.
Press the shutter release button the rest of the way to record the image.
Using the Macro Mode
The Macro Mode lets you focus automatically on close up subjects. The automatic focus operation starts when you press the shutter release button down half way. The following is the focus range in the Macro Mode.
Approximately 14cm to 50cm (5.5˝ to 19.7˝)
1.
Keep pressing display.
MF until the is on the
2.
Record the image.
• The focus and image recording operations are identical to those in the Auto Focus Mode.
• You can tell whether the image is focused by observing the focus frame and the green operation lamp. The indications of the focus frame and green operation lamp are the same as those in the Auto Focus Mode.
IMPORTANT!
• Optical zoom is disabled in the Macro Mode. Zoom is fixed at maximum wide angle.
54
OTHER RECORDING FUNCTIONS
Using the Infinity Mode
The Infinity Mode fixes focus at infinity (
∞
). Use this mode when recording scenery and other faraway images.
1.
Keep pressing display.
2.
Record the image.
MF until the is on the
Using Manual Focus
With the Manual Focus Mode, you can adjust the focus of an image manually. The following shows focus ranges in the
Macro Mode for two optical zoom factors.
Optical Zoom Factor
1X
3X
Approximate Focus Range
14cm (0.5´) to infinity (
∞
)
40cm (1.3´) to infinity (
∞
)
1.
Keep pressing
MF until MF is on the display.
• At this point, a boundary also appears on the display, indicating the part of the image that will be used for manual focus.
Boundary
55
OTHER RECORDING FUNCTIONS
2.
While watching the image on the monitor screen, use [ ] and
[ ] to focus.
Manual focus position
To do this:
Focus out on the subject
Focus in on the subject
Do this:
Press [ ].
Press [ ].
• Pressing [ ] or [ ] causes the area inside of the boundary displayed in step 1 to fill the monitor screen momentarily to aid in focus. The normal image reappears a short while later.
3.
Press the shutter release button to record the image.
56
OTHER RECORDING FUNCTIONS
Using Focus Lock
Focus lock is a technique you can use to focus on a subject that is not located within the focus frame when you record an image. You can use focus lock in the Auto Focus Mode and the Macro Mode ( ).
1.
Using the monitor screen, compose the image so the main subject is within the focus frame, and then press the shutter release button half way.
Focus frame
IN
• The focus and image recording operations are identical to those in the Auto Focus Mode.
• You can tell whether the image is focused by observing the focus frame and the green operation lamp. The indications of the focus frame and green operation lamp are the same as those in the Auto Focus Mode.
2.
Keeping the shutter release button half way down, re-compose the image as you like.
IN
3.
When the image is composed the way you want, press the shutter release button the rest of the way to record it.
NOTE
• Locking the focus also locks the exposure.
57
OTHER RECORDING FUNCTIONS
Exposure Compensation (EV Shift)
Exposure compensation lets you change the exposure setting (EV value) manually to adjust for the lighting of your subject. This feature helps to achieve better results when recording a backlit subject, a strongly lit subject indoors, and a subject that is against a dark background.
Exposure Compensation Range: –2.0EV to +2.0EV
Steps: 1/3EV
1.
In a recording mode, press [ ] and [ ].
• This causes the exposure compensation value to appear on the monitor screen.
EV value
Press [ ] to increase the EV value. A higher EV value is best used for light-colored subjects and backlight subjects.
Press [ ] to decrease the EV value. A lower EV value is best for dark-color subjects and for shooting outdoors on a clear day.
58
• To cancel exposure compensation, adjust the value until it becomes zero.
2.
Compose the image and then press the shutter relese button.
IMPORTANT!
• When shooting under very dark or very bright conditions, you may not be able to obtain satisfactory results even after performing exposure compensation.
OTHER RECORDING FUNCTIONS
Recording Consecutive Images
(Continuous Shutter Mode)
The Continuous Shutter Mode records images as long as you keep the shutter release button depressed. Note that the length of the interval between images depends on the image quality setting.
1.
Press / DPOF to select the Continuous
Shutter Mode (page
49).
• The Continuous Shutter
Mode is selected when the indicator is on the monitor screen.
2.
Hold down the shutter release button to record the images you want.
IMPORTANT!
• The flash does not fire during continuous shutter recording.
• You cannot use the self-timer in combination with the continuous shutter mode.
• Never remove the battery or memory card from the camera or unplug the AC adaptor while images are being saved to memory.
59
OTHER RECORDING FUNCTIONS
Combining Shots of Two People into a
Single Image (Coupling Shot)
The Coupling Shot Mode lets you record images of two people and combine them into a single image. This makes it possible for you to include yourself in group images, even when there is no one else around to record the image for you.
• First Image This is the part of the image that does not include the person who is recording the first image.
• Second
Image
Making sure that the background of the image is aligned correctly, record the image of the person who recorded the first image.
• Combined
Images
60
1.
Align the mode dial with (Coupling Shot
Mode).
2.
First, align the focus frame on the monitor screen with the subject you want on the left side of the image, and then press the shutter release button to record the image.
• The following settings are fixed for this image: focus, exposure, white balance, zoom, flash.
Focus frame
OTHER RECORDING FUNCTIONS
3.
Next, align the focus frame with the subject you want in the right side of the image, taking care to align the actual background with the semi-transparent image of the background of the first image, which is shown on the monitor screen. When everything is aligned correctly, record the image.
Semi-transparent image
• Pressing MENU any time after step 2 of the above procedure cancels the first image and returns to step
2.
NOTE
• The Best Shot Mode (page 64) includes three sample scenes that use Coupling Shot. One of the scenes uses two shots on the left half and the right half of the image, as described in the procedure above. The first shot of the other two Coupling Shot sample scenes uses the left 1/3 of the image, while that of the remaining sample scene uses the right 1/3 of the image.
Note, however, that the Coupling Shot sample scenes in the Best Shot Mode cannot be used in the Coupling
Shot Mode.
61
OTHER RECORDING FUNCTIONS
Recording a Subject onto an Existing
Background Image (Pre-shot)
Pre-shot helps you get the background you want, even if you need to ask someone else to record the image for you. Basically, Pre-shot is a two-step process.
1. You compose the background you want and press the shutter release button, which causes a semi-transparent image of the background to remain on the monitor screen.
2. Ask someone else to record a shot of you against your original background, telling them to compose the image by using the semi-transparent monitor screen image as a guide.
• The camera stores the image produced by step 2 only.
• Depending on how the image is actually composed in step 2, its background may not be exactly the same as the one you composed in step 1.
Note that Pre-shot is available in the Best Shot Mode only
(page 64).
• Freeze the background on the monitor screen.
• This records the image.
• Record the image, using the background on the monitor screen as a guide.
62
OTHER RECORDING FUNCTIONS
1.
Align the mode dial with
2.
Use [ ] and [ ] to select “Pre-shot,” and then press SET.
.
3.
Freeze the background on the monitor screen.
• Though a semi-transparent image of the background appears on the monitor screen in step 4, the background image is not saved in memory at this time.
• The following settings are fixed for this image: focus, exposure, white balance, zoom, flash.
4.
Next, align the focus frame with the subject, composing the subject with the semitransparent background shown on the monitor screen. When everything is aligned correctly, record the image.
Semi-transparent image
• This records the image composed on the monitor screen in step 4. The reference background image is not recorded.
• Pressing MENU any time after step 3 of the above procedure cancels the background image and returns to step 3.
63
OTHER RECORDING FUNCTIONS
Using the Best Shot Mode
Selecting one of the 33 Best Shot scenes automatically sets up the camera for recording a similar type of image.
■
Example Sample Scene
1.
Align the mode dial with .
• This enters the Best
Shot Mode and displays a sample scene.
■
Composition Outline
Selecting certain Best Shot scenes causes a composition outline to appear on the monitor screen. Use the composition outline to compose your image and achieve proper balance. The location of the composition outline depends on the sample scene you select.
Focus frame
Composition outline
Example: Recording a portrait.
64
2.
Use [ ] and [ ] to select the sample scene you want, and then press SET.
3.
Record the image.
IMPORTANT!
• Sample scenes numbered 5 through 7 are Coupling
Shot scenes (page 60). Sample scene number 8 is a
Pre-shot scene (page 62).
• Best Shot scenes were not recorded using this camera. They are provided as samples only.
• Images recorded using a Best Shot scene may not produce the results you expected due to shooting conditions and other factors.
• You can change to a different sample scene by using
[ ] and [ ] to select the scene you want and pressing
SET.
OTHER RECORDING FUNCTIONS
Creating Your Own Best Shot Setup
You can use the procedure below to save the setup of an image you recorded for later recall when you need it again.
Recalling a setup you save automatically sets up the camera accordingly.
1.
Align the mode dial with .
• This enters the Best Shot Mode and displays a sample scene.
2.
Use [ ] and [ ] to display “Register
Favorites.”
4.
Use [ ] and [ ] to display the image whose setup you want to register as a
Best Shot scene.
5.
Use [ ] and [ ] to select “Save,” and then press SET.
• This registers the setup.
• Now you can use the procedure on page 64 to select your user setup for recording.
3.
Press SET.
65
OTHER RECORDING FUNCTIONS
IMPORTANT!
• Setups that you register as Best Shot Mode sample scenes are located after the built-in sample scenes.
• Note that formatting the built-in memory (page 103) deletes all Best Shot Mode user setups.
NOTES
• Best Shot Mode user setups are located in memory after the built-in sample scenes.
• The following are the settings that are included in a
Best Shot Mode user setup: focus mode, EV shift value, filter, metering mode, white balance mode, color enhancement, flash intensity, sharpness, saturation, contrast, flash mode, ISO sensitivity, and aperture and shutter speed.
• Note that images recorded with this camera only can be used for registration of Best Shot Mode user setups.
• You can register up to 999 Best Shot Mode user setups.
• You can check the current setup of a scene by displaying the various setting menus.
• User setups are assigned file names using the format
“UQVR3nnn.jpe” (where n = 0 to 9) or “UQVR4nnn.jpe”
(where n = 0 to 9).
■
To delete a Best Shot Mode user setup
1.
Align the mode dial with .
• This enters the Best Shot Mode and displays a sample scene.
2.
Use [ ] and [ ] to display the user setup you want to delete.
3.
Press to delete the user setup.
• You can also delete a user setup by using your computer to delete its file in the “SCENE” folder in camera memory (page 122).
66
OTHER RECORDING FUNCTIONS
Using the Night Scene Mode
The night scene mode extends the exposure time to produce beautiful night images.
1.
Align the mode dial with .
2.
Record the image.
NOTE
• When recording a portrait of a subject against a twilight or nighttime background, you can use the Night Scene
Mode in combination with the flash to achieve a slow sync effect that causes the subject to stand out better.
IMPORTANT!
• Always mount the camera on a tripod when using the
Night Scene Mode. This protects against blurred images caused by slow shutter speeds.
• Auto Focus may not be able to work properly when lighting is low. If this happens, focus the image manually (page 55). Trying to record a fast moving object can cause blurring of the image.
• The slower the shutter speed, the more likely it is that the recorded image will not match the image that is on the monitor screen when you press the shutter release button.
67
Shooting with Manual Exposure
In the Manual Exposure Mode, you can manually adjust shutter speed and aperture.
• Shutter Speed Setting Range
Shutter Speed
Brightness
Movement
Slower
2 seconds
2 seconds
Brighter
Flowing
Faster
1/1000 second (F2.6)
1/2000 second (F5.0)
Darker
Stopped
• Aperture Setting Range
Aperture
Brightness
Focus
Wider Smaller
F2.6, F5.0 (Wide angle zoom)*
Brighter
Shallow
Darker
Deep
* The following shows how the optical zoom setting affects aperture.
Zoom
Wide Aperture
Small Aperture
(Wide Angle) (Telephoto)
F2.6/3.0/3.4/3.8/4.2/4.6/4.8
F5.0/5.8/6.5/7.3/8.0/8.7/9.2
OTHER RECORDING FUNCTIONS
1.
Align the mode dial with M (Manual Exposure).
2.
Use [ ] and [ ] to specify the shutter speed, and then use
[ ] and [ ] to specify the aperture value.
Shutter speed value
Aperture value
3.
Compose the image and then press the shutter release button.
IMPORTANT!
• The shutter speed and aperture value on the monitor screen will turn orange when you press the shutter release button half way if the image is over-exposed or under-exposed.
• You may not be able to achieve the brightness you want when recording an image that is very dark or very bright. If this happens, adjust the shutter speed.
• Using slow shutter speeds can cause static noise to appear in the image.
• At shutter speeds slower than 1/8 second, the brightness of recorded image may not be the same as the brightness of the image that appears on the monitor screen.
68
OTHER RECORDING FUNCTIONS
Using the Movie Mode
You can record movies up to 30 seconds long.
• File Format: AVI
AVI format conforms to the Motion JPEG format promoted by the Open DML Group.
• Image Size: 320 x 240 pixels
• Movie File Size: Approximately 200KB/second.
• Maximum Movie Length
— One Movie: 30 seconds
— Total Movie Time:
60 seconds with built-in memory; 330 seconds with
64MB SD memory card
1.
Align the mode dial with .
• “Remaining capacity” shows how many 30second movies can still be recorded to memory.
Remaining capacity
2.
Point the camera at the subject and then press the shutter release button.
• Movie recording continues for 30 seconds, or until you stop it by pressing the shutter release button again.
• The remaining recording time value counts down on the monitor screen as you record.
• If you want to stop recording sooner than 30 seconds, press the shutter release button again.
3.
After recording stops, the camera starts the movie file store operation.
• To cancel storage of the movie file while it is being performed, press , use [ ] and [ ] to select “Delete,” and then press SET.
IMPORTANT!
• The flash does not fire in the Movie Mode.
Remaining recording time
69
OTHER RECORDING FUNCTIONS
Shooting at Fixed Intervals
You can set up the camera to record at fixed intervals, specifying the number of images to be recorded, the interval between recordings, and a start time. The following describes the types of recording variations you can configure.
• Interval Recording
Records images at a fixed interval, starting immediately.
• Timer Recording
Records a single image at a specified time.
• Interval Timer Recording
Records images at a fixed interval, starting from a specified time.
70
1.
Align the mode dial with .
2.
Use [ ] and [ ] to change the “Shots” setting, and then press [ ].
• Specify the number of shots you want to record. Skip this step by pressing SET without changing the default setting (1) if you want to record a single image.
• Select the “MAX” option if you want recording to continue until memory becomes full.
3.
Use [ ] and [ ] to change the “Interval” setting, and then press [ ].
• Specify the interval between shots. You can specify a value from one minute to 60 minutes, in one-minute increments.
4.
Use [ ] and [ ] to set the start time, and then press SET.
• The initial default setting for the start time is “Start.”
• You can set the start time to a value in the range of 1 minute to 240 minutes. When you press the shutter release button in step 6, recording starts after the number of minutes you specify here passes.
• If you want recording to start immediately when you press the shutter release button, select “Start” for this setting, and then press SET to advance to the next step.
OTHER RECORDING FUNCTIONS
5.
Configure image recording settings.
• At this point, you should make white balance and any other settings you want.
6.
Align the focus frame with the subject, and then press the shutter release button all the way down.
• This causes camera power to turn off. Camera power will turn back on and image recording will be performed in accordance with the interval timer recording settings you configured with the above steps.
■
Canceling an Interval Mode Timer Operation
Turning on the camera while it is standing by for an Interval
Mode record operation causes the message “Interval recording was canceled.” to appear, and cancels the interval recording operation. An Interval Mode record operation is also cancelled by changing the mode dial setting to something other than .
71
OTHER RECORDING FUNCTIONS
Adjusting the White Balance
The wavelengths of the light produced by various light sources (sunlight, light bulb, etc.) can affect the color of a subject when it is recorded. White balance lets you make adjustments to compensate for different lighting types, to make the colors of an image appear more natural.
1.
In a recording mode, press MENU.
2.
Select the “REC” tab, select “White Balance,” and then press
[ ].
3.
Use [ ] and [ ] to change the current setting, and then press SET.
When shooting under these conditions:
Normal conditions
Outdoor daylight
Shade
Incandescent light bulb (reddish tinge)
Fluorescent light (greenish tinge)
Difficult lighting that requires manual control (See below.)
Select this setting:
Auto
Manual
NOTE
• Selecting “Manual” changes white balance to the settings achieved the last time a manual white balance operation was performed.
72
OTHER RECORDING FUNCTIONS
Adjusting White Balance Manually
Under some light sources, automatic white balance under the “Auto” setting can take a long time to complete. Also, the auto white balance range (color temperature range) is limited. Manual white balance helps to ensure that colors are recorded correctly for a particular light source.
Note that you must perform manual white balance under the same conditions you will be shooting under. You must also have a white piece of paper or other similar object on hand in order to perform manual white balance.
1.
In step 3 of the procedure under
“Adjusting the White
Balance,” select
“Manual” (page 72).
• This causes the object you last used to adjust manual white balance to appear on the monitor screen.
2.
Point the camera at a white piece of paper or similar object under the lighting conditions for which you want to set the white balance, and then press the shutter release button.
• This adjusts the white balance.
3.
Press SET.
• This registers the white balance settings and exits the setting screen.
• Dim lighting or pointing the camera at a dark colored object can cause white balance to take a long time to complete.
73
OTHER RECORDING FUNCTIONS
Selecting the Metering Mode
Use the following procedure to specify multi-pattern metering, spot metering, or center-weighted metering as the metering mode.
1.
In a recording mode, press MENU.
2.
Select the “REC” tab, select “Metering,” and then press [ ].
3.
Select the setting you want and then press
SET.
Multi-pattern:
Multi-pattern metering divides the image into sections and measures the light in each section for a balanced exposure reading. The camera automatically determines shooting conditions according to the measured lighting pattern, and makes exposure settings accordingly.
This type of metering provides error-free exposure settings for a wide range of shooting conditions.
74
Center-weighted:
Center-weighted metering measures light concentrating on the center of the focus area. Use this metering method when you want to exert some control over exposure, without leaving settings totally up to the camera.
Spot:
Spot metering takes readings at a very small area. Use this metering method when you want exposure to be set according to the brightness of a particular subject, without it being affected by surrounding conditions.
IMPORTANT!
• When “Multi” is selected as the metering mode, certain procedures cause the metering mode setting to change automatically as described below.
• Changing the exposure compensation setting (page
58) to a value other than 0.0 changes the metering mode setting to “Center Weighted.” The metering mode changes back to “Multi” when you return the exposure compensation setting to 0.0.
• Selecting manual exposure (page 67) changes the metering mode setting to “Center Weighted.” The metering mode changes back to “Multi” when you select an exposure mode other than manual.
OTHER RECORDING FUNCTIONS
Using the Histogram
Using the DISP button to display the histogram on the monitor screen makes it possible for you to check exposure conditions as you record images (page 20). You can also display the histogram of a recorded image in the Play Mode.
Histogram
A histogram is a graph that represents the lightness of an image in terms of the number of pixels. The vertical axis indicates the number of pixels, while the horizontal axis indicates lightness. You can use the histogram to determine whether an image includes the shadowing (left side), mid tones (center), and highlighting (right) required to bring out sufficient image detail. If the histogram appears too lopsided for some reason, you can use exposure compensation (EV shift) to move it left or right in order to achieve better balance. Optimum exposure can be achieved by correcting exposure so the graph is as close to the center as possible.
• When the histogram is too far to the left, it means that there are too many dark pixels.
This type of histogram results when the overall image is dark. A histogram that is too far to the left may result in
“black out” of the dark areas of an image.
• When the histogram is too far to the right, it means that there are too many light pixels.
This type of histogram results when the overall image is light. A histogram that is too far to the right may result in
“white out” of the light areas of an image.
• A centered histogram indicates that there is good distribution of light pixels and dark pixels. This type of histogram results when the overall image is at optimal lightness.
75
OTHER RECORDING FUNCTIONS
IMPORTANT!
• Note that the above histograms are shown for illustrative purposes only. You may not be able to achieve exactly the same shapes for particular subjects.
• A centered histogram does not necessarily guarantee optimum exposure. The recorded image may be overexposed or under-exposed, even though its histogram is centered.
• You may not be able to achieve an optimum histogram configuration due to the limitations of exposure compensation.
• Use of the flash or multi-metering, as well as certain shooting conditions can cause the histogram to indicate exposure that is different from the actual exposure of the image when it was recorded.
• When using the Continuous Shutter Mode, the histogram appears for the first image only (page 59).
• This histogram does not appear when you are using
Coupling Shot (page 60).
Recording Mode Settings
The following are the settings you can make before recording an image using a recording mode.
• ISO sensitivity
• Enhancement
• Color filtering
• Saturation
• Contrast
• Sharpness
• Grid on/off
• Power on default settings
NOTE
• You can also configure the settings listed below. See the referenced pages for more information.
— Size and Quality (page 51)
— White Balance (page 72)
— Metering (page 74)
— Flash Intensity (page 48)
— Digital Zoom (page 45)
76
OTHER RECORDING FUNCTIONS
Specifying Sensitivity
Use the following procedure to select the sensitivity setting that suits the type of image you are recording.
1.
In a recording mode, press MENU.
2.
Select the “REC” tab, select “ISO,” and then press [ ].
3.
Select the setting you want and then press
SET.
QV-R3
Auto : Automatic sensitivity selection
ISO125 : Conforms with ISO125
ISO250 : Conforms with ISO250
QV-R4
Auto : Automatic sensitivity selection
ISO100 : Conforms with ISO100
ISO200 : Conforms with ISO200
IMPORTANT!
• Increasing sensitivity can cause static to appear inside an image. Select the sensitivity setting that suits your shooting needs.
Enhancing Specific Colors
Use the following procedure when you want to enhance a particular color in your recorded image.
1.
In a recording mode, press MENU.
2.
Select the “REC” tab, select “Enhance,” and then press [ ].
3.
Select the setting you want and then press
SET.
To do this:
Turn off color enhancement
Enhance reds
Enhance greens
Enhance blues
Enhance flesh tones
Select this setting:
Off
Red
Green
Blue
Flesh Tones
NOTES
• Enhancing a color produces the same effect as attaching a color enhancer lens filter to the lens.
• If color enhancement and the filter function (page 78) are both turned on at the same time, the filter function is given priority (color enhancement is not performed).
77
OTHER RECORDING FUNCTIONS
Using the Filter Function
The camera’s filter function lets you alter the tint of an image when you record it.
1.
In a recording mode, press MENU.
2.
Select the “REC” tab, select “Filter,” and then press [ ].
3.
Select the setting you want and then press
SET.
• Available filter settings are: Off, B/W, Sepia, Red,
Green, Blue, Yellow, Pink, Purple
IMPORTANT!
• Using the camera’s filter feature produces the same effect as attaching a color filter to the lens.
• If color enhancement (page 77) and the filter function are both turned on at the same time, the filter function is given priority (color enhancement is not performed).
Specifying Color Saturation
Use the following procedure to control the intensity of the image you are recording.
1.
In a recording mode, press MENU.
2.
Select the “REC” tab, select “Saturation,” and then press [ ].
3.
Select the setting you want and then press
SET.
To get this:
High color saturation (intensity)
Normal color saturation (intensity)
Low color saturation (intensity)
Select this setting:
High
Normal
Low
78
OTHER RECORDING FUNCTIONS
Specifying Contrast
Use this procedure to adjust the relative difference between the light areas and dark areas of the image you are recording.
1.
In a recording mode, press MENU.
2.
Select the “REC” tab, select “Contrast,” and then press [ ].
3.
Select the setting you want and then press
SET.
To get this:
High contrast
Normal contrast
Low contrast
Select this setting:
High
Normal
Low
Specifying Outline Sharpness
Use the following procedure to control the sharpness of image outlines.
1.
In a recording mode, press MENU.
2.
Select the “REC” tab, select “Sharpness,” and then press [ ].
3.
Select the setting you want and then press
SET.
To get this:
High sharpness
Normal sharpness
Low sharpness
Select this setting:
Hard
Normal
Soft
79
OTHER RECORDING FUNCTIONS
Turning the On-screen Grid On and Off
You can display gridlines on the monitor screen to help you compose images and ensure that the camera is straight when recording.
1.
In a recording mode, press MENU.
2.
Select the “REC” tab, select “Grid,” and then press [ ].
3.
Select the setting you want and then press
SET.
To do this:
Display the grid
Hide the grid
Select this setting:
On
Off
Specifying Power On Default Settings
You can configure the camera to save certain settings in
“mode memory” when it is turned off, and restore them the next time you turn the camera back on. This keeps you from having to configure the camera each time you turn it on.
● Mode Memory Settings
The following are the settings that can be saved in mode memory and restored the next time you turn on the camera.
Flash mode, focus mode, white balance, ISO sensitivity, metering mode, flash intensity, digital zoom, manual focus position
1.
In a recording mode, press MENU.
2.
Select the “Memory” tab, and then press [ ].
3.
Select the item whose setting you want to change, and then press SET.
80
OTHER RECORDING FUNCTIONS
4.
Select the setting you want and then press
SET.
To do this:
Save the current status of the setting and restore it the next time the camera is turned on.
Restore the factory default setting whenever the camera is turned on.
Select this setting:
On
Off
5.
After you are finished configuring settings, press the MENU button to exit the setting screen.
On Function
Flash
Focus
White Balance
ISO
Metering
Flash Intensity
Digital Zoom
MF Position
Setting when camera is turned off
Off
Auto
Auto
Auto
Auto
Multi
Normal
On
Last Auto Focus position that was in effect before you switched to manual focus
81
Resetting the Camera
Use the following procedure to reset all of the camera’s settings to their initial defaults as shown under “Menu Reference” on page 131.
1.
In a recording mode or the Play Mode, press
MENU.
2.
Select the “Set Up” tab, select “Reset,” and then press [ ].
3.
Select “Reset,” and then press SET.
• To cancel the procedure without resetting, select
“Cancel” and press SET.
advertisement
* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Related manuals
advertisement
Table of contents
- 1 OTHER RECORDING FUNCTIONS
- 1 Selecting the Focus Mode
- 1 Using Auto Focus
- 2 Using the Macro Mode
- 3 Using the Infinity Mode
- 3 Using Manual Focus
- 5 Using Focus Lock
- 6 Exposure Compensation (EV Shift)
- 7 Recording Consecutive Images (Continuous Shutter Mode)
- 8 Combining Shots of Two People into a Single Image (Coupling Shot)
- 10 Recording a Subject onto an Existing Background Image (Pre-shot)
- 12 Using the Best Shot Mode
- 13 Creating Your Own Best Shot Setup
- 15 Using the Night Scene Mode
- 15 Shooting with Manual Exposure
- 17 Using the Movie Mode
- 18 Shooting at Fixed Intervals
- 20 Adjusting the White Balance
- 21 Adjusting White Balance Manually
- 22 Selecting the Metering Mode
- 23 Using the Histogram
- 24 Recording Mode Settings
- 25 Specifying Sensitivity
- 25 Enhancing Specific Colors
- 26 Using the Filter Function
- 26 Specifying Color Saturation
- 27 Specifying Contrast
- 27 Specifying Outline Sharpness
- 28 Turning the On-screen Grid On and Off
- 28 Specifying Power On Default Settings
- 29 Resetting the Camera
- 30 PLAYBACK
- 30 Basic Playback Operation
- 31 Zooming the Displayed Image
- 32 Resizing an Image
- 33 Cropping an Image
- 34 Playing a Movie
- 35 Displaying the 9-image View
- 36 Selecting a Specific Image in the 9-image View
- 37 DELETING FILES
- 37 Deleting a Single File
- 38 Deleting All Files
- 39 FILE MANAGEMENT
- 39 Folders
- 39 Memory Folders and Files
- 40 Protecting Files
- 40 To protect and unprotect a single file
- 40 To protect all files in memory
- 41 DPOF
- 41 To configure print settings for a single image
- 42 To configure print settings for all images
- 43 PRINT Image Matching II
- 43 Exif Print
- 44 OTHER SETTINGS
- 44 Specifying the File Name Serial Number Generation Method
- 44 Turning the Key Tone On and Off
- 45 Specifying an Image for the Startup Screen
- 45 Using the Alarm
- 45 To set an alarm
- 46 Stopping the Alarm
- 47 Changing the Date and Time Setting
- 47 Changing the Date Format
- 48 Using World Time
- 48 To switch between the home time and World Time screens
- 48 To configure World Time settings
- 49 To configure summer time (DST) settings
- 50 Changing the Display Language
- 51 Formatting Built-in Memory